Dermatology Flashcards
(224 cards)
6 functions of skin
protection, absorption, excretion, secretion, regulation, sensation
6 morphological things to describe
- palpability (indicated by shadow)
- Color
- Shape
- Texture
- Size
- Location
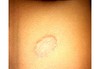
circumscribed; non-palpable discoloration of the skin; less than 1 cm

Macule
Primary lesion
ex: freckles and rubella
non palpable discoloration; irregular border; greater than 1 cm

Patch
Primary lesion
ex: vitiligo
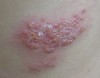
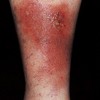
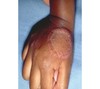
well-circumscribed; solid lesion; flat topped, plateau-like; greater than 1 cm
In Epidermis

Plaque
Primary lesion
ex: psoriasis, discoid lupus, erythematosus
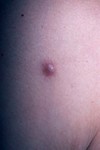
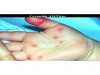
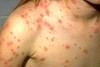
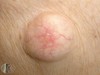
solid elevation; less than 1 cm

Papule
Primary lesion
ex: acne, warts, insect bites
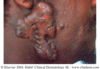
solid, palpable; circumscribed lesion; larger than a papule (> 1 cm)
smaller than a tumor; originates in dermal or subcutaneous tissue

Nodule
Primary lesion
ex: erythema nodosum, gouty tophi
solid, palpable, circumscribed lesion
> 2 cm
can be above, level or beneath skin surface
Tumor
Primary lesion
ex: lipoma
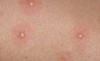
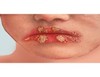
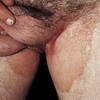
superficial, well-circumscribed, raised, fluid-filled lesion
contains serous fluid
less than 0.5 cm

Vesicle
Primary lesion
ex: herpes simplex, varicella (chickenpox)
superficial, well-circumscribed, raised, fluid filled lesion
> 0.5 cm
Epidermis
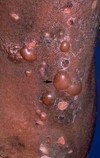
Bulla (blister)
Primary lesion
ex: bullous pemphigoid, pemphigus, dermatitis herpetiformis
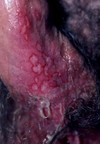
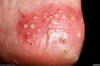
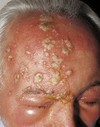
a vesicle filled with PURULENT fluid small, circumscribed

Pustule
Primary lesion
ex: acne, impetigo
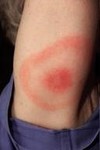
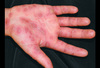
slightly raised, red, irregular, transient lesions,
secondary to edema of the skin
erythematous borders with pale centers epidermis

Wheal
Primary lesion
ex: urticarial (hives), allergic rxn to injections or insect bites
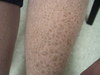
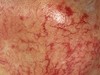
flat, non-blanching, red-purple lesions; caused by a hemorrhage to the skin
2 non-palpable types

Purpura
Primary lesion
- Petechia: less than 5 mm
- Ecchymosis (bruise): greater than 5 mm
SECONDARY LESION
visible shedding of stratum corneum
epidermal origin

Scale
ex: often seen with psoriasis
SECONDARY LESION
slightly raised; irregular border; variable color
resulting from dried blood, serum or other exudate
epidermis origin
Crust
ex: scab
SECONDARY LESION
depressed lesion; resulting from loss of epidermis due to rupture of vesicles or bullae; often caused by friction or pressure
heals WITHOUT scar confined to epidermis

Erosion
ex: rupture of herpes simplex blister
SECONDARY LESION
depressed lesion resulting from loss epidermis and part of dermis
HEALS WITH SCAR irregular size and shape

Ulcer
ex: decubitus ulcers, primary lesion of syphilis
SECONDARY LESION
deep linear lesion into the dermis; wedge-shaped in epidermis with abrupt walls
can extend into dermis

Fissure
ex: cracks in athlete’s foot
SECONDARY LESION
linear superficial lesion, may be covered with dried blood due to scratching of skin
*specific to itching

Excoriation
SECONDARY LESION
Thickening of epidermis, resulting in accentuation of skin lines results from chronic irritation and rubbing

Lichenification
ex: atopic dermatitis
SECONDARY LESION
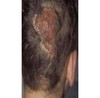
replacement of normal skin with fibrous tissue; often resulting from injury involved in deeper dermis
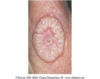
Scar
SECONDARY LESION
thinning or depression of the skin surface due to reduction of underlying tissue depression in epidermis

Atrophy
ex: aging, stretch marks
SECONDARY LESION
hardening of the skin caused by an increase in collagen, mucin, edema or cellular infiltration

Sclerosis
SECONDARY LESION
tissue death
Necrosis