Development L3 - Oral Development biology: Arches Flashcards
(22 cards)
In which week would you expect to see the appearance of pharyngeal arches
pharangyeal arches appear in 4th and 5th week.
where do neural crest cells migrate from to reach the pharyngeal arches
they migrate from the back of the developing head
how are the pharyngeal arches separated internally and externally
arches are separated by
clefts/grooves - externally
pouches - internally
neural crest cells migrate to the lower face to undergo proliferation and differentiation. which gene mediates neural crest cells.
hox gene
name the arches

pharyngeal arch 5 is misisng becuase it is removed very early on in embryo development.

pharyngeal arches consists of ectoderm and endoderm germ layers.
however these germ layers are located in specific locations on the pharyngeal arches. where are they located?
Ectoderm is located on the outside of the pharyngeal arches
Endoderm is located in the inside of the pharyngeal arches except for the 1st arch
what is the name given to the 1st pharyngeal arch and which processes are present
what is the name of the special cartilage present in 1st p arch
which two bones does this cartilage form
which two ligaments does this cartilage form
1st p arch is mandibular arch which houses the mandibular and maxillary processes
the special cartilage present is the meckels cartilage
the two bones the meckels cartilage devlops is the incus and malleus, which are two bones of the ear
the two ligaments produced are the sphenomandibular and the sphenomalleolar
which muscles, nerve and arterties does the 1st pharyngeal arch give rise to
the 1st pharangyeal arch is called the mandibular arch. so the muscles, nerve and blood supply will be generally associated with that arch.
muscle of mastication = temporalis, masseter, pterygoids, mylohyoid, anterior body of digastric
nerve = trigeminal
artery = maxillary and carotid arteries

what is the name given to the 2nd pharyngeal arch
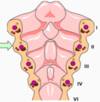
hyoid arch
which muscles, nerve, cartilage and gland does the 2nd pharyngeal arch give rise to
cartilage = reicherts cartilage, which gives rise to stapes, lesser horn and superior hyoid body, styloid process and stylohyoid ligament
muscles = facial expression and posterior belly digastric
nerve = facial VII
gland = thyroid gland and tonsil
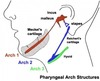
what are the arrows pointing to

clefts
the 2nd - 6th clefts disappear due to the proliferation of which arch
2nd arch (hyoid arch)
what is the arrow pointing to

pouch
the eustacian tube
middle ear cavity
tympanic membrane
ventral part obliterated by the tongue, would be found in which pouch
1st, 2nd or third pouch
1st pouch
the tonsillar fossa
ventral part obliterated by the tongue, would be found in which pouch
1st, 2nd or third pouch
2nd pouch
which pouch would house the inferior parathyroid gland and thymus
1st, 2nd or 3rd pouch
3rd pouch
which pouch would house the superior parathyroid gland
1st, 2nd, 3rd or 4th pouch
4th pouch
the vagus nerve is present in which pouch
4th pouch
the glossopharyngeal nerve is present in which pouch
third pouch
the internal carotid artery is present in which pouch
third pouch
the right subclavian artery and aorta are present in which pouch
pouch 4


