Development of the Midgut and Hindgut Flashcards
(125 cards)
What does the midgut give rise to?
- Small intestine, including most of the duodenum post bile duct entry
- Caecum and appendix
- Ascending colon
- Proximal 2/3 or transverse colon
Draw a diagram illustrating the position of the midgut in an embryo

What causes the midgut to make a loop?
It elongates enormously, and quickly runs out of space due to the large size of the developing liver
What does the loop made by the midgut have at its axis?
The superior mesenteric artery
What is the loop made by the midgut connected to?
The yolk sac
How is the midgut loop connected to the yolk sac?
By the vitelline duct
What are the limbs of the midgut loop called?
Cranial and caudal limbs
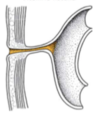
Label this diagram

- A - Cranial limb
- B - Superior mesenteric artery at axis
- C - Caudal limb
- D - Vitelline duct to yolk sac
- SMA
- Cranial
- Caudal
What are the derivatives of the cranial limb?
- Distal duodenum
- Jejunum
- Proximal ileum
What are the derivates of the caudal limb?
- Distal ileum
- Cecum
- Appendix
- Ascending colon
- Proximal 2/3 of transverse colon
What happens to the primary loop during the 6th week of development?
It elongates very rapidly
What happens to the liver during the 6th week of development?
It grows very rapidly
What is the problem with the rapid growth of both the liver and the primary loop?
The abdominal cavity is too small to accomodate both
What is the result of the abdominal cavity being too small too accomodate the primary loop and the liver?
Physiological herniation
What is physiological herniation?
Where the intestines herniate into the proximal umbilical cord, alongside the umbilical vessels
What are the stages in rotation of the midgut loop?
- First rotation
- Second rotation
By how much is the first rotation of the midgut loop?
90 degrees
By how much is the second rotation of the midgut loop?
180 degrees
What happens in the first rotation of the midgut loop?
During herniation into the umbilical cord, the midgut rotates around the axis formed by the SMA in a counter clockwise direction (cranial limb moves to back, caudal to the front)
Draw a diagram illustrating what happens in the first rotation of the midgut loop?

Does elongation of the small intestinal lumen continue during rotation?
Yes
What is the result of the elongation of the small intestinal loop continuing during rotation?
The jejunum and ileum form a number of coiled loops
What happens to the large intestine during rotation?
It lengthens, but does not participate in the coiling phenomenon
When does the second rotation of the midgut loop occur?
When it returns into the abdominal cavity, around week 10