DNA Flashcards
(41 cards)
DNA
Genes make proteins. Contains Thymine, is Double Stranded, contains Deoxyribose Sugar.
Genome
The complete sequence of nucleotides of its DNA.
Chromosome
3 billion base pairs distributed across 46 chromosomes (made of DNA and Proteins) which form 23 pairs
Nitrogenous Bases
Cytosine, Thymine, Adenine, and Guanine
RNA
Contains Uracil, is Single Stranded, contains Ribose sugar.
DNA => Protein
DNA is copied by mRNA and brought out from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. tRNA changes codons (three rungs) into amino acids which create proteins. This process if called Protein Synthesis
Autoradiography
Take Thymine (only found in DNA) and mark it with radioactivity so is was made visible after some months on a screen.
DNA Replication
Occurs during birth, growth, and repair. 1. Helicase binds at the origin of replication site 2. Helicase unwinds the DNA, cutting the hydrogen bonds between the base pairs 3. DNA Polymerase adds free floating nucleotides to compliment the template strands - DNA Polymerase can only add from the 5’ to 3’ direction of the strand - Okazaki fragments are formed on the 5’ to 3’ side of the unwound strand * The Okazaki fragments are connected by DNA Ligase (an enzyme)
Watson & Crick
Stole Roseland Franklin’s idea of discovering DNA’s shape through X-Ray Crystallography and they recieved all the credit
Meselson & Stahl
Proved that DNA is semi-conservative.
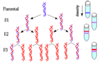
Protein Synthesis
DNA is copied by mRNA and brought out from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. tRNA changes codons (three rungs) into amino acids which create proteins.
Transcription
- Initiation - RNA Polymerase binds to the promoter region 2. Elongation - RNA Polymerase slides down the strand, splitting the two strands - As the RNA Polymerase reseals the DNA as it passes by - RNA Polymerase brings in free floating RNA nucleotides complementary to the antisense strand to form the mRNA - Only adds from the 3’ to 5’ direction mRNA strand is 5’ to 3’, Antisense strand is 3’ to 5’ 3. Termination - The RNA Polymerase and mRNA strands fall off at the termination point.
Mutations
Mutations are random changes to the base sequence in a gene during Transcription. Frameshift - Deletion - Insertion Substitution
Sickle Cell Anemia
Substitution of the T nucleotide with the A nucleotide which results in creating Valine (GUG) instead of Glutamic Acid (GAG). This affects the shape of red blood cells, giving those with the trait a sickled shape. This disease is prevalent in areas where Malaria is rampant because having the Sickle Cell trait provides immunity to Malaria.
mRNA Splicing
- Put on a cap to protect the strand from: - Being chopped up outside of the nucleus - From enzymes in the cytoplasm 2. Cut out introns (‘intruders’) - Reassemble the exons, leaves the nucleus to the cytoplasm
Translation
- Initiation - mRNA enters, tRNA binds mRNA enters the ribosome - The start tRNA (Methionine) binds in the P site with the start codon, AUG 2. Elongation - new tRNA enters, Methionine jumps, Ribosome shifts, old tRNA ejects - The second tRNA enters the A site according to codons on the mRNA - The Methionine jumps onto the amino acids carried by the tRNA that just entered the A site - Ribosome shifts by one codon, ejecting the tRNA which moved to the E site 3. Termination - when a tRNA binds to a stop codon and the chain of polypeptides detaches. - Proteins can be various lengths.
Genetic Code
The genetic code is degenerate which means, there is more than one codon to represent certain amino acids. The genetic code is universal, all living organisms make proteins the same way.
Polymerase Chain Reaction
The goal is to amplify DNA to have enough to perform gel electrophoresis. 1. Once the target DNA is located TAQ polymerase is extracted from hot springs because they are heat-resistant and added together in a test tube. DNA is then denatured. - 95 °F breaks the hydrogen bonds and splits open the DNA. 2. Temperature decreases to 60 °F so the primers can anneal (attach). - The temperature is increased to 72 °F and TAQ Polymerase is added.
Gel Electrophoresis
STRs or Short Tandem Repeats are sequences of repeated nucleotides. These repeats differ between individuals. These can identify individuals by targeting DNA then isolating and cleaving the different sections using Restriction Enzymes then insert them into wells in agarose gel. This machine has a positive and negative pole and once it’s turned on it pulls the negatively charged DNA towards that pole. It moves the smaller pieces of STRs closer to the pole showing different bands of different sized DNA.
DNA Transformation
DNA transformation is a process by which DNA can be transferred into. bacteria.
Genetic Engineering
- Isolate the Insulin Production Gene with Restriction Enzymes - This leaves sticky ends (or uneven DNA sequences at the end of the strands) 2. Isolate a bacterial plasmid and cut it with the same Restriction Enzymes 3. Insert gene into plasmid using complementary base-pairing and Ligase - Insert recombinant plasmid into bacterial cell (Transformation)
Cloning
- An adult somatic cell was isolated from a sheep’s udder 2. An egg cell (gamete) is isolated from another cell 3. Isolate the nucleus out of the egg cell 4. Electricity combines the somatic cell and the enucleated egg cell 5. Starve the cell to prompt division
Karyotyping
amniocentesis to ensure the health of a fetus.
Meiosis
Only occurs in ovaries or testes in egg cells or sperm cells (gametes). The goal is to create haploid gametes, containing half the amount of chromosomes in diploid cells. Meiosis begins with 4 chromosomes.