Dr. Mhawi 4 Overview of the Epithelium Flashcards
(118 cards)
True or False: epithelium is avascular
True
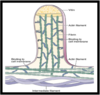
Explain the general characteristics of epithelium
8.5.7

8.5.7
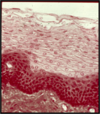
Explain this image

EPITHELIOIDS:
–lack a free surface
Epithelioid organization typically found in endocrine glands:
–islets of Langerhans in the pancreas
–interstitial cells of LEYDIG in testis
–luteal cells of ovary
–adrenal gland
–many epithelium-derived tumors
What are the 6 functions of epithelium and give an example?
Secretion
- Epithelium lining trachea and bronchial tree secretes mucus
- Epithelium lining Stomach secretes mucus and gastric juice
Absorption:
- As in the epithelium of the intestine and the proximal convoluted tubules of the kidney
Transport:
- As in transport of materials along the surface of epithelium by motile cilia
Protection:
- Water barrier of the stratified squamous epithelium of the skin
- melanocyte protect against UV light
Sensation:
–Epithelial cells involved in sensation are called neuroepithelial cells
Sensation:
–Epithelial cells involved in sensation are called neuroepithelial cells
nBarrier:
–Epithelial cells lining the intestine and/or blood vessels are joined to each other by tight junctions (AKA Occluding junctions)
________ is one cell-thick layer of flat cells
SIMPLE SQUAMOUS
–lines blood and lymphatic vessels
–wall of Bowman’s capsule in kidney
–lines the walls and covers the content of the abdominal and thoracic cavities
–lines respiratory alveoli of the lung
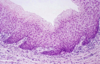
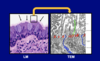
Explain this image

8.5.7
Section of a vein. All blood vessels are lined with a simple squamous epithelium called endothelium (arrowheads). Smooth muscle cells in the vein wall are indicated by arrows. Pararosaniline-toluidine blue (PT) stain
8.5.7
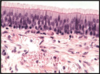
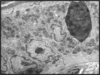
Explain this image
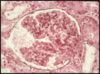
8.5.7
Simple squamous epithelium (arrows) in the wall of the Bowman’s capsule of the kidney.
8.5.7
Special Terminologies for the Simple Squamous
_______ –name given to simple squamous epithelia lining blood and lymph vessels and the ventricles and atria of the heart
_______ name for simple squamous epithelia that line walls and cover contents of closed cavities of body:
- Abdominal cavity
- thoracic cavity
Endothelium
Mesothelium
8.5.7
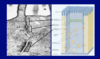
Explain this image

8.5.7
Endothelium

- 5.7
- 5.7
Explain this image
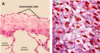
8.5.7
A, light micrograph of the mesothelial cells covering the lung (pleura). B, Cells of the simple squamous epithelium in general appears as tiles with centrally located nuclei when viewed tangentially (from the top).
8.5.7
Explain this image

Light micrograph of the mesothelial cell covering the mesentery (connective tissue covering the intestine).
What ate the two exceptions to sqamous classification
–post capillary venules of the lymph nodes
- AKA high endothelial venules
- endothelial cells are cuboidal (arrowheads)
–venous sinuses of spleen
§endothelial cells are rod-shaped
–Called stave cells

____ are one cell-thick layer of cubic (cuboidal) cells
SIMPLE CUBOIDAL
–found in:
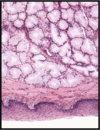
§wall of thyroid follicles
§walls of kidney tubules
§surface of ovary (germinal layer)
8.5.7
Explain this image

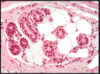
Walls of thyroid gland is made of simple cuboidal epithelium. Arrows point to capillaries.
8.5.7
Explain this image

Simple cuboidal epithelium from kidney collecting ducts (upper part of the ducts).
______ are one cell-thick layer of tall cells
SIMPLE COLUMNAR
–lines:
§intestinal tract from stomach to rectum
§uterus and cervix
§kidney collecting ducts
8.5.7
Explain this image

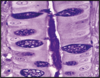
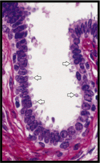
Small intestine lumen is lined by simple columnar epithelium. Goblet cells specialized in secreting mucus (stained magenta) are also visible.
8.5.7

Explain this image
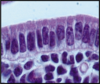
Simple columnar epithelium covers the inner cavity of the uterus. Note that the epithelium (E) is separated from the underlying loose connective tissue of the lamina propria (LP) by a basal lamina (BL). The epithelium, basal lamina and lamina propria constitute the mucosa. H&E stain.
8.5.7
Explain this image

8.5.7
Simple columnar epithelium from the kidney collecting ducts (lower parts of the ducts).
8.5.7
Explain this image

Fundic stomach lined by simple columnar epithelium. PAS stain.
_____ are two-cell or more epithelium
Stratified
Types
–Stratified squamous
§Keratinized and non-keratinized
–Stratified cuboidal
–Stratified columnar
–Transitional
____ superficial layer is squamous that functions as a barrier
STRATIFIED SQUAMOUS
nLocation:
–Epidermis
–lining of oral cavity
–lips
–lining of esophagus
–lining of vagina
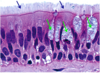
Explain this image

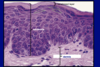
Expalin this image
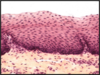
8.5.7
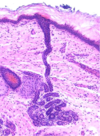
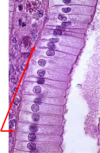
Esophagus, stratified squamous nonkeratinized. Arrow points to a longitudinal section of blood vessel. Remember, epithelial tissue is avascularized tissue. Nutrients diffuse from the underlying blood vessels.
8.5.7