drugs Flashcards
(351 cards)
<p></p>
<p>Methotrexate</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<ul>
<li>Antimetabolite</li>
<li>AntifolateChemotherapy (Folic acid analog)</li>
<li>Cytotoxic Agent (target all dividing cells)</li>
</ul>
<p></p>
<p></p>

<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
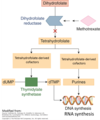
<p>Mechanism of action of methotrexate: What is the primary target?</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p>Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) </p>

<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p>Mechanism of action of methotrexate</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p>Reduces synthesis of purines
Reduces synthesis of dTMP by inhibiting the necessary cofactor for thymidylate synthetase
Reduces cellular proliferation and induces cellular death by preventing synthesis of RNA and DNA
</p>
<p><p><p><p>Methotrexate therapeutic uses </p></p></p></p>
<p><p><p><p>Useful as single agent in treating acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children
Osteosarcomas often treated with high doses.
Choriocarcinoma (cancer in women’s womb that often originates from placental precursor cells)
Cure rate is 75-90 % with sequential treatments with methotrexate and dactinomycin.
Part of combination therapy for some types of lymphomas, leukemias, and cancers of the breast, head and neck, ovary, and bladder.
</p></p></p></p>
<p><p><p><p>Methotrexate therapeutic uses </p></p></p></p>
<p><p><p><p>Useful as single agent in treating acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children
Osteosarcomas often treated with high doses.
Choriocarcinoma (cancer in women’s womb that often originates from placental precursor cells)
Cure rate is 75-90 % with sequential treatments with methotrexate and dactinomycin.
Part of combination therapy for some types of lymphomas, leukemias, and cancers of the breast, head and neck, ovary, and bladder.
</p></p></p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p>How do you reduce Methotrexate toxicity?</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<ul>
<li>Leucovorin rescue</li>
<li>Leucovorin is administered after and otherwise lethal dose of methotrexate is administered.</li>
</ul>

<p><p><p><p>Methotrexate Resistance</p>
| </p></p></p>
<p><p><p><ul>
<li>Impaired transport</li>
<li>Altered forms of DHFR with decreased affinity for methotrexate</li>
<li>Elevated DHFR expression (gene amplification)</li>
<li>Numerous other mechanisms</li>
</ul>
</p></p></p>
<p><p><p><p>Methotrexate Toxicities</p>
| </p></p></p>
<p><p><p><p>Nephrotoxicity</p>
| </p></p></p>
<p><p><p><p>5-fluorouracil (5-FU) (4 things)</p>
| </p></p></p>
<p><p><p><ul> <li>inhibits thymidylate synthase</li> <li>Pyrimidine Analog</li> <li>Antimetabolite</li> <li>Cytotoxi Agent</li> </ul> </p></p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p>Mechanism of action of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU)</p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<ul>
<li>5-FU is metabolized into 5-fluorodeoxyuridine monophosphate (FdUMP), which inhibits thymidylate synthase.</li>
<li>Causes DNA damage by decreasing thymidylate (dTMP) levels, leading to cell death</li>
</ul>

<p><p><p><p>Capecitabine (4 things)</p>
| </p></p></p>
<p><p><p><ul> <li>Antimetabolite</li> <li>Pyrimidine analog</li> <li>is a prodrug of 5-FU that had improved oral bioavailability allowing it to be given orally.</li> <li>Cytotoxic Agent</li> </ul> </p></p></p>
<p><p><p><p>Resistance to 5-FU can be associated with </p></p></p></p>
<p><p><p><p>amplification of thymidylate synthetase.
| </p></p></p></p>
<p><p><p><p>5-FU used as a component of </p></p></p></p>
<p><p><p><p>chemotherapy regimens for breast cancer, head and neck cancers, colorectal, and gastrointestinal.
</p></p></p></p>
<p><p><p><p>5-FU Rarely used as</p></p></p></p>
<p><p><p><p>a single agent
| </p></p></p></p>
<p><p><p><p>5-FU Adverse effects </p></p></p></p>
<p><p><p><p>include oral and GI ulcers and bone marrow suppression
</p></p></p></p>
<p><p><p><p>Capecitabine (3 things)</p></p></p></p>
<p><p><p><p>Antimetabolite
Pyrimidine analog
is a prodrug of 5-FU that had improved oral bioavailability allowing it to be given orally.
</p></p></p></p>
<p><p><p><p>Most important antimetabolite to treat acute myelogenous leukemia (AML)</p>
</p></p></p>
<p><p><p><ul>
<li>Cytarabine (cytosine arabinoside, ara-C)</li>
<li>Only used in treatment of hematologic malignancies</li>
<li>Ara-C is an analog of cytosine.</li>
</ul>
</p></p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p>Ara-CTP incorporation into DNA inhibits </p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p>DNA polymerase, thus halting elongation of DNA molecules</p>

<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p>Cytarabine (cytosine arabinoside, ara-C) Only active in </p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p>S-Phase</p>

<p><p><p><p>Cytidine deaminase inactivates </p></p></p></p>
<p><p><p><p>ara-C.
| </p></p></p></p>
<p><p><p><p>Cytarabine clinical toxicities</p>
| </p></p></p>
<p><p><p><ul>
<li>Cytidine deaminase levels are quite low in the central nervous system. CNS exposed to higher concentrations than the rest of the body.
<ul>
<li>Can cause cerebellar syndrome Dysarthria (motor speech disorder)</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li>Toxicity is strongly correlated with renal dysfunction, hepatic dysfunction, and advancing age.<br></br>
</li>
</ul>
</p></p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p>Gemcitabine resistance
| </p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p>Reduced activity of deoxycytidine kinase
Tumors increasing production of deoxycytidine
</p>

<p><p><p><p>Cytarabine (3)</p>
| </p></p></p>
<p><p><p><ul> <li>Antimetabolite</li> <li>Pyrimidine analog</li> <li>Cytotoxic Agent</li> </ul> </p></p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<p>Gemcitabine(3)</p>
<p></p><p></p><p></p><ul> <li>Antimetabolite</li> <li>Pyrimidine analog</li> <li>Cytotoxic agent</li> </ul>
Gemcitabine Cytotoxic effects
- Incorporated into DNA, which inhibits synthesis and function
- Inhibits ribonucleotide reductase (reduces pools of dNTPs, which are necessary for DNA synthesis

Gemcitabine used in treatment of
a wide range of cancers including: pancreatic, non–small cell lung, ovarian, bladder, etc…
Gemcitabine resistance
|Reduced activity of deoxycytidine kinase Tumors increasing production of deoxycytidine
6-Thioguanine (6-TG) (4)
- Cytotoxic agent
- Antimetabolite
- Purine analog
- treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemis.
6-Mercaptopurine (6-MP) (4)
- Cytotoxic agent
- antimetabolite
- Purine analog
- Treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia

6-Thioguanine (6-TG) 6-Mercaptopurine (6-MP)
- 6-MP was the first purine analog used in cancer chemotherapy
- Treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)
- Largely replaced by newer antipurines fludarabine and cladribine
Mechanism of action of 6-TG (6-Thioguanine)
- activated to thio-GMP and thio-IMP hypoxanthine-guanine phospho- ribosyl transferase (HGPRT).
- Decreased activity of HGPRT common mechanism of resistance.
- Thiopurine methyltransferase (TPMT) inactivates 6-MP.
- Common gene variant (polymorphism) causes reduced TPMT activity.
- Can lead to life-threatening toxicity

Mechanism of action of 6-Mercaptopurine (6-MP)
- activated to thio-GMP and thio-IMP hypoxanthine-guanine phospho- ribosyl transferase (HGPRT).
- Decreased activity of HGPRT common mechanism of resistance.
- Thiopurine methyltransferase (TPMT) inactivates 6-MP.
- Common gene variant (polymorphism) causes reduced TPMT activity.
- Can lead to life-threatening toxicity

Fludarabine (4)
- Cytotoxic agent
- antimetabolite
- newer purine analog
- Commonly used to treat chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) by itself or in combination with cyclophosphamide and rituximab.

Fludarabine Mechanism
- Deoxycytidine kinase activates drug in cells by converting it to the tri-phosphate form.
- Incorporated into DNA and RNA
- Inhibits DNA polymerase and ribonucleotide reductase (RNR)
- Inhibits RNA function, including mRNA translation into proteins

Fludarabine resistance
commonly caused be decreased activity of deoxycytidine kinase and drug efflux.
Cladribine (4)
- Cytotoxic Agent
- Newer purine analog
- antimetabolite
- Standard therapy for hairy cell leukemia (HCL) (curative intent) "when your HAIR gets wet it DRIPS"--> claDRIBine

Cladribine Mechanism
- Deoxycytidine kinase activates drug in cells by converting it to the tri-phosphate form.
- Incorporated into DNA
- Causes strand breaks
- Potent inhibitor of ribonucleotide reductase (RNR)
Cladribine resistance
commonly is associated with decreased activity of deoxycytidine kinase, drug efflux, and increased RNR expression
Methotrexate Mechanism
|Inhibits dihydrofolate reductase, which reduces precursors for RNA and DNA synthesis
5-fluorouracil (5-FU) | Mechanism
Incorporated into DNA and RNA, which inhibits synthesis and function Inhibits thymidylate synthetase, which reduces DNA precursors
Cytarabine (ara-C) | mechanism
Incorporated into DNA and RNA, which inhibits synthesis and function Inhibits DNA synthesis by inhibiting DNA polymerase
Gemcitabine Mechanism
Incorporated into DNA, which inhibits synthesis and function Inhibits ribonucleotide reductase (RNR), which reduces precursors for DNA
6-MP and 6-TG | Mechanism
Incorporated into DNA, which inhibits synthesis and function Reduce precursors for RNA and DNA by inhibiting purine synthesis
Cladribine | Mechanism
Incorporated into DNA Causes strand breaks Potent inhibitor of ribonucleotide reductase (RNR), which reduces DNA precursors
Cladribine | Mechanism
Incorporated into DNA Causes strand breaks Potent inhibitor of ribonucleotide reductase (RNR), which reduces DNA precursors
General mechanisms of alkylating agents
- Among the oldest and most useful class
- Reactions between alkyl groups on drug with nucleophilic groups on proteins and nucleic acids
- Most common binding site is seven-nitrogen group of guanine
- Cause DNA crosslinking and strand breakage

Alkylating agents
Cytotoxic cell cycle nonspecific agents (they are toxic in all stages of cell cycle)
Common alkylating agents
|- Nitrogen mustards
- Related to the ‘mustard gas’ used during the First World War
- Examples include: Mechlorethamine, cyclophosphamide, chlorambucil, and ifosfamide
- Nitrosoureas
- Carmustine (BCNU) and lomustine
Cyclophosphamide (4)
- Cytotoxic Agent
- Alkylating agent
- Nitrogen Mustard
- most commonly used alkylating agent in both solid tumors and hematological malignancies.
- Hemorrhagic cystitis caused by acrolein (5-10% of patients)

mesna
- Co-administration of mesna (with cyclophosphamide), a sulfhydryl compound, inactivates acrolein (cytotoxic to bladder cells).
- Reduces risk of hemorrhagic cystitis
Resistance to alkylating agents
Inactivation by glutathione and other nucleophiles (increased glutathione production) Reduced uptake Accelerated DNA repair Increased expression of O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) MGMT prevents permanent DNA damage by removing alkyl groups from guanine before cross-links form

Resistance to alkylating agents
|- Inactivation by glutathione and other nucleophiles (increased glutathione production)
- Reduced uptake
- Accelerated DNA repair
- Increased expression of O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT)
- MGMT prevents permanent DNA damage by removing alkyl groups from guanine before cross-links form
Non-classical alkylating agents
(Platinum compounds) Considered non-classical alkylating agents because while they lead to DNA cross-linkages, they have no alkyl group like the classical alkylating agents. Targets nucleophilic center (primarily at guanine-N7 Actively transported into cells via a Cu2+ transporter
Cisplatin
1st generation platinum agent cytotixic agent non-classical alkylating agent platinum analog
```Carboplatin
2nd generation platinum agent cytotixic agent non-classical alkylating agent platinum analog
```Oxaliplatin
3rd generation platinum agent cytotixic agent non-classical alkylating agent platinum analog
Non-classical alkylating agents | Commonly used to
ovarian, testicular, head and neck, bladder, esophagus, lung, and colon cancers
Cisplatin | adverse effects
Anaphylactic-like reactions (hypersensitivity reactions) Peripheral motor and sensory neuropathy Nephrotoxicity Can be significantly reduced by increasing hydration by co-administering intravenous saline
Cisplatin | adverse effects
Anaphylactic-like reactions (hypersensitivity reactions) Peripheral motor and sensory neuropathy Nephrotoxicity Can be significantly reduced by increasing hydration by co-administering intravenous saline
Vinblastine
- Cytotoxic agent
- Plant dericatives and similar compounds
- vinca alkaloid (from periwinkle plant)
- Antimicrotubule agents
Vincristine
- Cytotoxic agent
- Plant dericatives and similar compounds
- vinca alkaloid (from periwinkle plant)
- Antimicrotubule agents

Adverse effects of vincristine |
Mostly neurological (numbness and tingling in extremities, motor weakness)
Paclitaxel (taxol)
- Cytotoxic agent
- Plant derivatives and similar compounds
- Taxanes
- Antimicrotubule agents

Paclitaxel (taxol) mechanism
Paclitaxel kills tumor cells by arresting them in mitosis by preventing the depolymerization of microtubules.
Paclitaxel (taxol) adverse effect
peripheral neuropathy |
filgrastim
- (granulocyte-colony stimulating factor) used often with Paclitaxel to reduce myelosuppression
- Hypersensitivity allergic reactions occur in about 5 % of the patients receiving paclitaxel.
- This is largely prevented when patients are pretreated with dexamethasone and anti-histamines.
irinotecan
- cytotoxic agent
- plant derivative and similar compound
- camptothecins analog
- induce cytotoxicity by inhibiting topoisomerase I (prevents repair of cuts leading to DNA damage).
Etoposide
- cytotoxic agent
- plant derivative and similar compound
- other
- is a class II topoisomerase inhibitor


