E1, L5 Flashcards
(49 cards)
Is DNA during interphase organized?
Yes! To allow for appropriate cellular machinery to access
What 3 DNA sequences are required?
origin of replication (where DNA replication begins), centromere (region where mitotic spindle attaches, assisting in lining up chromosomes and pulling to opposite poles), telomere (at the ends of linear chromosomes protecting them, made of telomeric DNA + proteins)
What do centromeres and telomeres contain in terms of DNA sequence?
Specific DNA sequences that bind specific proteins, highly compacted
What are genes?
DNA sequences that produce a functional RNA molecule (encodes a protein or forms a structural or regulatory RNA). They are comprised of exons, usually introns, and regulatory regions
What percentage of human DNA is unique sequences?
50%
heterochromatin
doesn’t contain expressed genes, tightly wound up
euchromatin
contains expressed genes, more open
exon
coding region of DNA, 1.5% of DNA
What are non-repetitive sequences usually? (ones that are not introns or exons)
regulatory sequences, promoters, enhancers, non-coding RNA
What do for repetitive sequences usually code for?
telomeres, centromeres, LINES, SINES, retroviral RNA elements
What are LINES or SINES
long/short intervening sequences
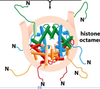
nucleosome
protein-DNA complex
Desribe the components of the nucleosome core protein
consists of 8 subunits, 2 H2A, 2 H2B, 2 H3, 2 H4
Describe the core proteins in terms of dimers that form, tetramer, and the overall structure?
H2A/H2B form a dimer, H3/H4 form a dimer. The H3/H4 dimers form a tetramer since H3 molecules interact with each other
The tetramer forms the center, and DNA wraps around this portion. The H2A/H2B dimers are on the outside on opp ends
Core protein structure illustration
How many DNA basepairs does the nucleosome contain?
~200
How many DNA basepairs wrap around the core protein? How many H-bonds?
147 DNA basepairs, 142 H-Bonds
What is the dimension of the beads on the string?
11 nm
How many times does DNA wrap around the core protein?
1.67 times
Where are the N-terminals of the histone subunits?
On the outside
Describe the core histone proteins?
they all (H2A, H2B, HC, HD) histone folds (3 a-helicle structures), as well a N-terminal tail and a very short C-terminal
Compare features of highly condenses and less condensed chromatin
Highly condenses is not as active, not used as much. Heterochromatin. Less condenses is more metabolically active, used more often. Euchromatin
How long does the wrapped nucleosome exist for? How long does the unwrapped exist for?
250 miliseconds, 10-15 miliseconds
What helps in unwrapping DNA and allows chromain to be dynamic?
ATP Dependent Chromatin Remodeling Complexes