ECGs Flashcards
(34 cards)
identify this ECG

Sinus arrhythmia
Identify this ECG

1st degree heart block
Identify this ECG

type 2 heart block, mobitz type 1
Identify this ECG

type2 heart block, mobitz type 2
Identify this ECG

3rd degree heart block
Identify this ECG

Atrial fibrillation
Identify this ECG

hyperkalaemia
Identify this ECG
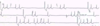
sick sinus syndrome
Identify this ECG

sinus bradycardia
Identify this ECG

Sinus tachycardia
Identify this ECG

supraventricular premature beats
Identify this ECG

supraventricular tachycardia
Identify this ECG

ventricular premature contractions
Identify this ECG

ventricular tachycardia
Identify this ECG

wandering pacemaker
Name non pathological arrhythmias
(2)
sinus arrhythmia
wandering pacemaker
Name the pathological bradyarrhythmias
8
type 1 heart block
type 2 heart block mobitz type 1
type 2 heart block mobitz type 2
type 3 heart block
sinus bradycardia
hyperkalaemia
hypokalaemia
sick sinus syndrome
Name the pathological tachyarrhyhmias
7
ventricular fibrillation
ventricular tachycardia
supraventricular tachycardia
atrial fibrillation
supraventricular premature beats
ventricular premature contractions
sinus tachycradia
Describe wandering pacemaker
Heart rate low to mid normal
Associated with sinus arrthymia
Variable amplitude or morphology of P wave
Change in P waves gradually shifts from normal to abnormal
non pathological
List differentials for sinus bradycardia
- Increased parasympathetic tone-
- respiratory disease
- gastric irritation
- increased CSF pressure
- Hypothyroidism
- Hypothermia
- Hyperkalaemia
- Hypoglycaemia
- Drug therapy
Describe type 1 heart block
Prolonged PR interval
P for every QRS
Due to prolonged conduction across the
AV node
Associated with increased parasympathetic
tone
May be due to drugs - digoxin, calcium
channel blocker, procainamide, beta-
blocker
PR interval can increase with age
May be completely normal for that
dog
Often there are no haemodynamic
abnormalities
No treatment is required
Describe type 2 heart block, mobitz type 1
P wave not followed by QRS
PR interval gradually prolongs until
blocked
QRS appears normal
The PR interval immediately preceding
the blocked beat is longer than the PR
interval immediately following the
blocked beat
Due to prolonged conduction across the AV
node
Associated with increased parasympathetic
tone
May be a normal variant
Can be induced by digoxin
Infrequently requires treatment
Describe type 2 heart block, mobitz type 2
P wave not followed by QRS
Often has wide QRS complexes
PR is of constant duration
May have multiple P waves not
followed by QRS e.g. 2:1, 3:1 etc
Caused by failure of impulse to
propagate through the Bundle of His or
bundle branches
Associated with organic disease of the
Bundle of His e.g. ischaemia, scarring,
infection, necrosis, granuloma or
tumour
Usually not responsive to atropine or
glycopyrrolate
Can cause reduced cardiac output if
ventricular response rate low
May require treatment if there are clinical
signs
Potential pacemaker candidate
Describe type 3 heart block
Atrial rate and rhythm that occurs
independently of a much slower
ventricular rate and rhythm
The ventricular rhythm is an escape from
latent, subsidiary pacemaker foci
QRS may look normal or may be
abnormal depending on the origin of the
impulse
Due to the same aetiologies as for Mobitz
type II block
Can be a consequence of Lyme disease
Cause signs of low output
No response to atropine
May be associated with hypothyroidism
Indication for a pacemaker



