Economics Theories Flashcards
(23 cards)
What is Fiscal Policy?
Changing the levels of taxation and government spending to influence aggregate demand in an economy.
What is expansionary Fiscal Policy?
- Increase in government spending
- Decrease taxation

What is contractionary Fiscal Policy?
- Decrease in government spending
- Increase in taxes
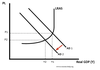
Critisism of Fiscal Policy
- Government have poor information
- Time Lags
- Crowd out private sector through borrowing, so less private investments
- Gov spend is inefficient
- Higher borrowing costs
Evaluation of Fiscal Policy?
- Depends on size of mulitplier
- State of the economy
- Depends on other factors in the economy
- Bond yields
Demand Pull Inflation?
Increase in AD
- Excessive public sector borrowing
- Cheap credit
- Housing boom

Cost Push Inflation
Increase in AS cost, shifting it left.
- Rising wage costs
- Fall in exchange rate

What are the aims of supply side policies?
- Reduce production costs to make firms more competitive
Examples of Supply Side Policies?
- Education
- Traning
- Industrial Policy
- R&D Subsidies
- Infrastructure
- Entrepreneurship
2 Types of Supply Side Policies?
Free-Market: involve policies to increase competitiveness and free-market efficiency.
Interventionist: government intervention to overcome market failure
Supply Side Policy Diagram?
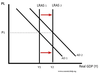
Benefits of Supply Side Policies?
- Lower inflation
- Lower unemployment
- Improved economic growth
- Improved BOP
Examples of Free-Market SSP?
- Privatisation
- Deregulation
- Reducing income tax
- Deregulate labour markets
- Increase free-trade
- Reducing unemployment benefits
- Remove red tape
Laffer Curve

Minimum Wage Diagram?

Advantages of Minimum Wage?
- Greater equity
- Reduced poverty
- Less worker expolitation by labour market monopolists
Disadvantages of Minimum Wage?
- Inflation
- Falling employment
- Competitiveness of UK exports
- Inflexible labour market
- Investment cuts
Monopoly Diagram?

Phillips Curve?

Perfect Competition?

Advantages of Oliogopolies?
- Highly competitive strategy
- Dynamically efficient
- Price stability
Disadvantages of Oligopolies?
- High concentration reduces choice
- Higher prices, less output
- Manipulating consumer decisions
- Barriers to entry
- Loss of economic welfare
- Allocatively and productively inefficient
Kinked Demand Curve?



