Ectoparasites of Ruminants Flashcards
(58 cards)
what is the generation time for lice
~3-5 weeks
what is the generation time for mange mites
~2-3 weeks
what is the survival off the host for lice
3-7 days
what is the survival off the host for mites
up to 3 weeks
what is the survival off the host for chorioptes
up to 10 weeks
what are the cattle lice species
- biting/chewing lice: Bovicola bovis
- sucking lice:
- long nosed cattle louse: Linognathus vituli
- short nosed louse: uncommon: Solenopotes capillatus
- little blue cattle louse: uncommon Haematopinus eurysternus
what are the predilection sites of cattle lice
sucking lice (head, neck):
- Linognathus vituli
- Solenopotes capillatus
- Haematopinus eurysternus
Biting lice (withers, back):
- Bovicola bovis
what are mange mites of cattle
Chewing mites:
- Chorioptes bovis
Burrowing mite:
- Sarcoptes scabiei
Sucking mite
- Psoroptes ovis
what are the mange common sites
Head/neck mange:
- Sarcoptes scabiei
Body mange:
- Psoroptes bovis
Heel/tail mange:
- Chorioptes bovis
what are the lesions of chorioptic mange
Classically discrete lesions in the skin folds on either side of the tail with little inflammation
Lesions can be more extensive in that region with more marked dermatitis and self inflicted traumatic damage to skin

what are risk factors of severe chorioptic mange
House
Stanchion
Straw bedding
Poor condition
what are the risk factors of psoroptic mange
Light color
Belgian blues
Charollais
what are the lesions of psoroptic mange like
Inflammation, exudation
hypersensitivity
Mites at periphery
what lice species is this

Bovicola bovis
what lice species is this

Linognathus vituli
what lice species is this

Solenopotes capillatus
what species of lice is this

Haematopinus eurysternus
what specie of lice is this

bovicola bovis
rounded mouthparts
what species of lice is this

piercing mouthparts
what species of mange mite is this

Chorioptes bovis
what species of mange mite is this

Sarcoptes scabiei
what species of mange mite is this

psoroptes ovis
what species of mange mite is this
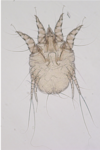
psoroptic mange
what sarcoptic mange lesions like
Thick crusts
Hyperkeratosis
Intensely pruritic
Self trauma