EM Test Flashcards
(209 cards)
ekg big box time
5 mm
200 msec
suture for superficial face
6-0 non absorbable
what cardiac marker peaks first?
myoglobin - peak sin 1-4, baseline in 18-24
treatment for distal radius fracture
reduction and sugar tong splint
Causes of second degree heart block mobitz I
Drugs: beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, digoxin, amiodarone
Increased vagal tone (e.g. athletes)
Inferior MI
Myocarditis
Following cardiac surgery (mitral valve repair, Tetralogy of Fallot repair
Rarely require pacemakers, usually benign

memory of sutures
high memory = stiff, hard to handle, come untied
low memory =
lower frequency ultrasound
greater penetration –> deeper imaging but lower resolution
thumb spica splint
for scaphoid fracture

what size should bites be in suturing?
- Bite size: ¼-in bites at 90 degrees create wound eversion
- Needle driver placement: 1/2-2/3 back from tip
*
- Needle driver placement: 1/2-2/3 back from tip
when do inflammatory reactions to suture peak?
first 2-7 days
scaphoid fracture mechanism
FOOSH
snuffbox tenderness
risk for avascular necrosis
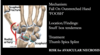
Sgarbossa Criteria
MI diagnosis in LBBB
- Concordant ST elevation > 1mm in leads with a positive QRS complex (score 5)
- Concordant ST depression > 1 mm in V1-V3 (score 3)
- Excessively discordant ST elevation > 5 mm in leads with a negative QRS complex (score 2).
- A total score of ≥ 3 has a specificity of 90% for diagnosing myocardial infarction
which sutures have the best strength?
polydiaxone/polygyconate

when to use horizontal mattress stitches?
- Horizontal mattress is good for use on fragile skin and also for areas of high tension; risk is that it holds so well that it can cause necrosis of the skin involved – best to only use when absolutely necessary
traquetrum fracture mechanism
hyperextension or hyperflexion injury

palms/soles suture removal time
10-12 days
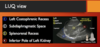
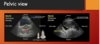
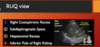
FAST indications
- hypotensive truma pt
- tachy trauma pt
- dyspneic trauma pt
- suspect pneumothorax or hemothorax
- suspect abd injury
higher frequency ultrasound
lesser penetration –> superficial imaging at higher resolution
what type of ACS requires hospital admission
unstable angina, NSTEMI, STEMI
asx CAD and SA can be outpaitnet wrokup
smiths fracture
volar displacement of distal wrist fracture
suture elasticity
degree to which suture stretches and returns to original length
vessel for inferior MI
RCA
abdominal probe
low frequency curivlinear
- 2-5 MHz
- Greater depth, broader field

anteroseptal MI
ST elevation is maximal in the anteroseptal leads (V1-4).
Q waves are present in the septal leads (V1-2).
There is also some subtle STE in I, aVL and V5, with reciprocal ST depression in lead III.
There are hyperacute (peaked ) T waves in V2-4.
These features indicate a hyperacute anteroseptal STEMI