Embryology Organogenesis Flashcards
(42 cards)
What are the derivatives of the ectoderm?
- Central nervous system
- Peripheral nervous system
- Epidermis, Hair, Nails
- Sensory epithelium (nose, ear, eye)

What are the derivatives of the mesoderm?
paraxial division: Skull, muscles, vertebrae
intermediate division: urogenital system
Lateral plate: serous membranes around organs (visceral layer) , body wall & limbs (parietal layer)
What are the derivatives of the endoderm?
Gut tube and its derivatives: glands, lungs, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
During week 3, the outer ectoderm undergoes neurulation. What are the three germ layers not our creative?
- Surface ectoderm (integumentary system)
- Neural tube (CNS)
- Neural crest cells (PNS)

What structures of the central nervous system are derived from the neural tube?
- Brain
- Spinal cord
- Posterior pituitary
Define the neural plate.
Pear-shaped thickening of ectoderm induced by the notochord and prechordal mesoderm.
(forms the CNS)

How is the neural tube formed?
The lateral edges (neural folds) of the neural plate approach each other and fuse (cranially to caudally) from a cervical region

Define neuropores. When do they close? What do they form?
- Partially incomplete fusion of the neural folds
- Day 25
- Cephalically forms the brain and the spinal cord caudally

Define neural crest.
Special Band of ectodermal cells on the neural fold that migrate into the mesoderm, proliferate, and form important structures.
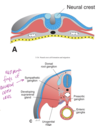
Which structures are neural crest derivatives?
- Spinal ganglia
- Sensory ganglia of cranial nerves V, VII, IX, X
- Autonomic ganglia
- Adrenal medulla
- Schwann cells
- Connective tissue of the anterior part of the skull and meninges
- Melanocytes
- C cells of the thyroid gland
- conotruncal septum of the heart

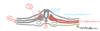
- axial mesoderm becomes the notochord
- paraxial mesoderm becomes somites
- Intermediate mesoderm becomes the reproductive and urinary system
- Lateral plate music becomes splanchnic and somatic divisions
What are the paraxial mesoderm somites?
- Sclerotome (vertebrae, ribs, occipital bone)
- Somite dermatome (skin over spine in epaxial region)
- Syndetome (tendons)
- Myotome (skeletal muscle)

Which tissues are derived from the somatic lateral plate mesoderm (SoLPM)?
Connective tissue, bones and smooth muscle

Which tissues are derived from the splanchnic lateral plate mesoderm (SpLPM)?
- Connective tissue and smooth muscle associated with the visceral inner tube
- Endothelium of blood vessels arteries and veins
- cardiac muscle

How does blood vessel formation occur?
- In the extraembryonic mesoderm surrounding the yolk sac at 3 weeks, then migrates.
- Later, it forms within the lateral plate mesoderm of the embryo.

GI tract is formed due to what process?
lateral and cephalocaudal folding of the fetal trilaminar disc.
(somites grow down and pinch off gute tube and also pull the amnion around the embryo)

What causes cephalocaudal folding of the fetal trilaminar disc?
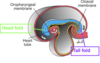
- Growth of brain ventricles
- lengthening of embryonic axis
(closes the body wall around the umbilical ring, forming the Primitive umbilical cord from the connecting stalk and the vitelline duct (yolk stalk)).

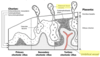
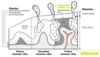
What sites in the uterus are considered normal sites for implantation?
Fundus (posterior, usually) AND body

Upon implantation what happens to the trophoblast?
It differentiates into two layers:
- the syncytiotrophoblast (outer layer)
- the cytotrophoblast (inner layer)

Define syncytiotrophoblast.
- Secretes human chorionic gonadotropin
- The outer layer which erodes endometrium and allows implantation

What does the cytotrophoblast become?
Syncytiotrophoblast

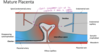
What does the fetus rely on for nourishment until the establishment of a placenta in week 12?
Embrytroph and the yolk sac
Describe how the primitive uteroplacental circulation is established.
- Syncytiotrophoblast invades endometrium
- Lacuna are formed in the uterine wall and filled with embryotroph
- Embryo invades deeper into the uterine wall and is completely embedded and covered by day 12

Define embrytroph.
Ruptured uterine capillaries and glands.
(Lacunae in the syncitiotrophoblast are filled with embryotroph, which nourishes the fetus until placenta is established)