Embryology Questions Flashcards
(184 cards)
what is present in the 2nd week of development of the extraembryonic cavity?
exocoelomic cysts
in IVF, what is used to stimulate ovaries?
Gonadotrophins
On which day does the posterior neuropore close?
day 27
which of the following are derived from the endoderm?
none of the following
which embryonic layer is in contact with the parietal hypoblast?
Cytotrophobast
which layer is generated by the epiblast?
epiblast
which layers are the primary villi originated from?
cytotrophoblast
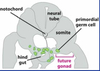
what structure is under the neural tube?
notochord
how long does semen capacitation take?
10 hours
what is the placenta?
haemochoral
what is the percentage of sperm in a sample?
14-90%
on which day does the process of allantosis begin?
day 15-16
when does the second meosis of oogenesis occur?
fertilisation
at the eigth day of development, the hypoblast consists of
small cuboidal cells
The amniotic cavity is formed by cells of the
epiblast
approximately how long after fertilisation does the first cleavage of the zygote occur?
30 hours
the primitive endothelial cells are formed by?
cells lining the yolk sac
in the beginning of the third week, the paraxial mesoderm differentiates into segments known as
somites
which embryonic layer is in direct contact with the parietal hypoblast until the formation of the extraembryonic mesoderm?
cytotrphoblast
monozygous twins may have
common amnion, placenta and chorion
the intraembryonic lateral plate mesoderm generates which of the following?
limb buds
which of the statements regarding the types of spermatogonia is NOT true?
stem cells generating sertolli cells
the number of oogonia at birth is approximately?
700,000-2,000000
the primitive endothelial cells are formed by?
cell linings of the yolk sac