emergency ENT - copied toE EXAMS Flashcards
(24 cards)

Ludwig’s angina is a form of severe diffuse cellulitis with bilateral involvement, primarily of the submandibular space.
It presents with an acute onset and spreads very rapidly meaning early diagnosis and immediate treatment planning is key to saving lives
What must never be missed and could cause avascular necrosis?
septal haematoma
(swelling from the medial side of a fractured nose)
What causes hot potato voice and tender, swollen lymph nodes?

A progressively severe sore throat on one side, odynophagia, usually are the earliest symptoms.
As the abscess develops, persistent pain in the peritonsillar area, fever, a general sense of feeling unwell, headache and a distortion of vowels informally known as “hot potato voice” may appear. Neck pain associated with tender, swollen lymph nodes, referred ear pain and foul breath are also common.
PTA should be specifically considered if there is limited ability to open the mouth (trismus).
main clinical features of AOM (acute otitis media)
otalgia
fever and deafness
otorrhoea
children; pain often worse at night
Otitis media bugs
haemophilus influenzae
streptococcus pneumoniae
moraxella catarrhalis
if viral then short-lived and self-limiting.
Management of Otitis media
analgesia. 80% improve spontaneously.
>48hrs require antibiotics

osteoma
more in males, unilateral.
often at junction of bony and cartilaginous ear canal.

AOM

Anatomy

otomycosis
Treatment, presentation and organism of malignant otitis externa

tympanic membrane normal
Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection which becomes invasive and erodes the temporal bone.
(diabetics are risk group)
>> Offensive discharge, chronic, pain, headaches
abx: ciprofloxacin
(amoxicillin for otitis media)
Flucloxacillin if uncomplicated otitis externa + signs of systemic infection

Rinne test
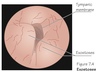
Exostoses
broad based and bilateral.
wax can collect behind.
cold water swimmers; inflammatory response to extremes of temperature.
What is found here?
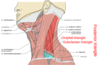
- SOLID:
- lymph nodes, cervical rib
- CYSTIC:
- cystic hygroma (lymphangioma)
- Pharyngeal pouch
- Subclavian aneurysm
*
Name some cystic lumps

- Branchial cyst
- Cystic degeneration of tumour
- Larynogocoele
Parotid tail lump - Solid
What other solid lumps are there?

- lymph node
- tumours
- vagal schwannoma
What’s this? + info.

Thyroglossal cysts
asymptomatic midline neck mass at or below the level of the hyoid bone, above the thyroid cartilage.
Most often in the midline
They may present in childhood (less than 50%) or, usually as a young adult < 20 years.
Move up when the tongue is protruded & with swallowing- cysts attached to the base of the tongue by the thyroglossal tract.
What lumps move with swallowing?
SOLID:
Goitre
lymph node
CYSTIC:
Thyroid cyst
What is FNAC?
Fine Needle Aspiration for Cytology
- may be used for neck lumps
Some possible red flags for neck lumps
Dark colour suggestive of malignant melanoma,
ulceration,
skin fixation,
bleeding, or
hard texture
Otitis Externa

Otitis externa results from a disturbance of the lipid/acid balance of the ear canal.
It is most usually infectious but may be caused by allergies, irritants or inflammatory conditions (all of which may also underlie bacterial infection).
Infection of the outer ear is usually bacterial (90%) or fungal (10%)[4]. Staphylococcus aureus and/or P. aeruginosa.
Fungal infection usually follows prolonged treatment with antibiotics, with or without steroids. About 10% of cases are fungal. 90% of fungal infections involve Aspergillus spp. and the rest are Candida spp.
Herpes zoster (Ramsay Hunt syndrome).
Infection may be localised to an infected hair follicle, causing a furuncle or localised otitis externa (S. aureus is the usual infecting organism).
What is Ramsay Hunt Syndrome?
Ramsay Hunt syndrome; varicella-zoster virus (chickenpox) becomes reactivated in the geniculate ganglion of the VIIth cranial nerve (facial nerve) causing facial paralysis, loss of taste, vestibulocochlear dysfunction and pain.
As a general rule, shingles is a disease of sensory nerves but Ramsay Hunt syndrome is distinctive in that there is a motor component.
How does an acoustic neuroma present?
should always be considered in patients with unilateral sensorineural deafness or tinnitus.
NB. otosclerosis causes a conductive deafness, and symptoms are bilateral.
What could a unilateral nasal polyp be a red flag sign for?
nasopharyngeal cancer and therefore warrant an urgent referral to ENT.
bilateral nasal polyps require non-urgent referral and topical corticosteroid therapy is first-line management.


