End of Year Exam Flashcards
(105 cards)
What is number 1? What does it do?

Ear Canal. Channels sound from outside to the eardrum.
What is number 2? What does it do?
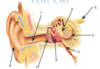
Inner Ear. A sealed cavity with a fixed air pressure. The ear drum presses down/stretches out and moves, it changes the pressure in the ear, causing the cillia to move.
What is number 3? What does it do?

Auditory Nerve. Transmits nerve signals from the cochlea to the brain, where the sound can be processed.
What is number 4? What does it do?

Cochlea. The Cochlea uses little hairs called cillia which move and convert movement into electrical signals which are passed to the auditory nerve.
What is number 5? What does it do?

Eustachian Tube. To maintain the correct air pressure for normal hearing.
What is number 6? What does it do?

Middle Ear. The bones move which create changes in pressure.
What is number 7? What does it do?

Eardrum. The sound travels untill it hits the eardrum causing it to move and vibrate.
What is number 8? What does it do?

Pinna. It collects sound and acting as a funnel amplifies this and directs it to the auditory canal.
What is the order of processes sound takes through the ear.
Pinna, Auditory/Ear Canal, Ear drum, Middle Ear (Bones -Hammer, Anvil, Stirrup), Inner Ear, Cochlea, Auditory Nerve.
Identify the concave and convex mirrors.

Convex is on the left and Concave is on the right.
How does a concave mirror reflect light?

The ray diagram shows that concave mirrors reflect light rays inwards. This causes the reflected rays to converge towards a focal point.
How does a convex mirror reflect light?
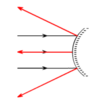
The ray digram shows that light rays are reflected outwards by convex mirrors. The reflected rays diverge so there is no focal point in front of the mirror.
What is refraction?
Refraction is light hitting an object and being refracted through the object so the light comes out the other side. Refraction is the beding of light as it changes medium from less to more dense vice-versa. The angle gets smaller when going from a less dense to more dense environemtn. The angle gets bigger when going from a more dense to less dense environment.
Draw a ray diagram showing refraction.
What is number 1?

The angles of incidence.
What is number 2?
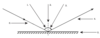
The normal.
What is number 3?
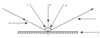
The angle of reflection.
What is number 4?

The reflected ray.
What is number 5?
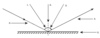
The mirror.
What is number 6?

The incident ray.
What is specular (regular) reflection?
If a bundle of light rays is incident upon a smooth surface, then the light rays reflect and remain in a bundle upon leaving the surface
What is diffuse reflection?
Reflection off rough surfaces such as clothing, paper, and concrete leads to a type of reflection known as diffuse reflection. If a bundle of light rays is incident to a rough surface, the light rays will reflect and diffuse in many different directions.
What does ROY G BIV stand for?
The colours of the rainbow. Red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet.
What are the three primary colours?
Red, green, and blue.


