Endocrine 1 Flashcards
(29 cards)
define homeostasis
The conceptual framework for the study/understanding of physiology
who is Claude Bernard
Father of modern Physiology
concept “our internal environment remains remarkably consistent despite changes in the external milieu”
>provides stable conditions for body cells
who is Walter Cannon
Coined the term “homeostasis”
describes the relative stability of the internal environment
what does homeostatic control rely on ?
sensor : constant monitoring
integrating centre : to coordinate
response system : to change
Most systems operate in a negatice feedback manner
what are the basic components of homeostatic system

Basic endocrine dysfunctions
Hyperfunction : too much hormone
Hypofunction : too little hormone
Resistance : too little effect
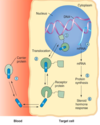
what is an endocrine gland ?
a tissue which releases (secretes) a substance into the bloodstream; this substance then travels via the blood to influence a target cell
describe the minkowski experiment
Discovery of Insulin
- Surgically removed pancreas ⇒ dog develops symptoms of diabetes
- Implant pieces of pancreas under skin ⇒ prevents symptoms of diabetes
What is the banting & best experiment
Discovery of Insulin
- identified antidiabetic substance in pancreatic extracts
- injected extracts prevents symptoms of diabetes (prevents elevated blood glucose)
Insulin as a hormone
peptide hormone produced by the beta cells of the pancreas
promotes absorption of glucose from blood to sketetal muscle and fat tissue
Inactive stored form = hexamer, zinc ion and histidine residues holding together
active = monomer
Kinds of hormones
- Most are proteins & polypepide
- steroids (cholesterol derivatives)
- Amines (catecholamines)
- Amins (thyroid)
levels of hormones effect
autocrine; made by cell and acts on same cell
paracrine; made by cell and acts on neighbouring cell
endocrine; made by cell and passes through bloodstream to another cell
mode of secretion for peptides
synthesis : in advance
storage : secretory vesicles
release from cell : exocytosis
transport in blood : dissolved in plasma
half life : short
example : insulin
mode of secretion for steroids
synthesis : on demand
storage : N/A
release from cell : diffusion
transport in blood : bound to carrier proteins
half life : long
example : estrogen/androgen
mode of secretion for amine (catecholamines)
synthesis : in advance
storage : secretory vesicles
release : exocytosis
transport in blood : dissolved in plasma
half life : short
example : epinepherine/norepinepherine
mode of secretion of amines (thyroid)
synthesis : in advance
storage : secretory vesicles
release from cell : diffusion
transport in blood : bound to carrier proteins
half life : long
example : thyroxine (T4)
conditions of receptor binding
- very high specificity for a particular hormone, but non-specific binding does occur (eg hormone “overspill”)
- there is a continuous turn-over of the receptor-hormone complex (essential for any signaling system)
where are receptors found
receptors for most hormones are found in the plasma membrane of target cells
receptors for steroid and thyroid hormones are inside the target cell; steroid in cytoplasm & thyroid in nucleus
Receptor Binding : transmembrane receptors (Overview)
- the hormone binds to the extracellular domain of the receptor and activates one or more cytoplasmic signalling pathways
- many of these pathways involve phosphorylation and enzyme activation
- some of these pathways lead to the DNA/mRNA/protein pathway response
- others just have a local effect in the target cell
Adenylate cyclase pathways
1) hormone and receptor bind; G proteins dissociate
2) A-subunit activates AC
3) catalyzes production of cAMP
4) removes regulatory unit from phosphate kinase
5) PK activates other molecules - hormonal response

Epinepherine binds what receptor in the adenylate cyclase pathway
beta-adrenergic receptors
Phospolipase C-Ca2+ receptor binding
1) hormone + receptor
2) G-proteins dissociate; activates PLC
3) causes breakdown of membrane phopholipid tp IP3
4) IP3 binds endoplasmic reticulum; releases stored Ca2+ into cytoplasm
5) Ca2+ activates other molecules - hormonal response

epinepherine binds what receptor in PIPLC
alpha-adrenergic