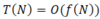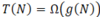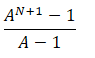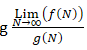Exam 1 Flashcards
(524 cards)
Reversed Card
A formula in which some number in a sequence depends on the previous numbers in a sequence.
What is a recurrence relation?
How does a skip list search work?
A search proceeds along the list with the greatest span until two references are found that enclose the required key. Then the search proceeds at the next level down until the required key found, or is deemed to be not present.
Reversed Card
LIFO
Stacks are sometimes known as ______ lists.
What is the findMin algorithm?
- FindMin(BinaryNode t)
- if(t==null) return null;
- if(t.left==null) return t;
- return findMin(t.left);
What is the Preorder traversal algorithm?
- DFSPre(Node X)
- If(X!=null)
- Do Work at Node
- DFSPre(x.left)
- DFSPre(x.right)
- If(X!=null)
Reversed Card
it allows GenericClass m = new GenericClass(); to be written simply as GenericClass m = new GenericClass<>();
What does the diamond operator do?
What four methods make up the simplest linked list interface?
Addathead
RemoveAtHead
Clear
isEmpty
How much space does merge sort require?
2n
Reversed Card
One takes only an object as an argument
One takes an object and a nextNode as arguments
When making a linked list, we use two constructors, what are their differences?
What a wrapper class?
A data type that stores a primitive type and adds extra functionality and methods to be used on the primitive type.
What is the PostOrder traversal algorithm?
- DFSPost
- If(X!=null)
- DFSPost(x.left)
- DFSPost(x.right)
- Do work
- If(X!=null)
Reversed Card
Finding the insertion point.
What is the first step to doing an insertion or deletion in a probabilistic skip list?
Classes that extend the iterable interface can implement what?
The enhanced for loop.
Reversed Card
- Guess the result and prove it by induction.
- Expand the recurrence by repeatedly substituting it into itself.
- The general solution method.
What are the three main ways to solve recurrence relations?

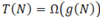
Reversed Card
An amortized runtime means that the runtime could be as large as O(n), but if m consecutive calls are made to the member functions, the runtime is MO(logN).
What is amortized runtime?
Reversed Card
It enables additions and deletions at either end of the list.
How is a deque different?
What is the linear time algorithm for the positive max subsequence problem?
Public static int maxsubsum(int[] a)
Int max sum = 0, this sum =0;
For (int I =0, I < a.length, i++)
Thissum += a[i];
If(thissum > maxsum ) maxsum = thissum;
Else if (thissum < 0) thissum = 0;
Return maxsum;
What are the two modes of insert in a red-black tree?
Top down insert and bottom up insert
Reversed Card
Reading the data (from disk)
When using an efficient algorithm, what is generally the bottleneck?
Reversed Card
A perfect binary tree of all black nodes.
What is embedded in every Red-Black tree?
What is a doubly linked list?
A list in which every node maintains a link to its previous and next node.
What is the suggested probabilistic variable value for a probabilistic skip list?
.25
Reversed Card
2n+2
What is the T(n) of a for loop from 1-n?