Exam 1 Flashcards
(35 cards)
The nuclear envelope is made up of two layers of ___ and is continuous with the ___
- Phospholipids
- Endoplasmic Reticulum
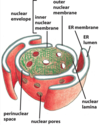
This allows passage through the two phospholipid membranes
Nuclear pore complex

Provides the structural component to the nuclear envelope
Nuclear lamina

Where is heterochromatin located?
On the periphery of the nucleus

What must proteins have to enter into the nucleus?
Nuclear Localization Signal (NLS)
What is chromatin and where is it located?
Complex of DNA and protein, and is found
in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells
What are histones?
Name all the histones
- Proteins that are responsible for the first level of DNA packing in chromatin
- H2A (2), H2B (2), H3 (2), H4 (2), and H1 (linker)
How large is the genome in terms of bps and genes?
- 3.2 X 109 base pairs
- 25,000 genes
What is the average gene size in terms of bps and exons?
What percentage of the genome is made up of exons?
- 27,000 bp
- 10.4 exons
- 1.5%
What is a ribosome composed of?
rRNA + proteins (ribonucleoprotein)
What takes place at the fibrillar regions of the nucleus?
rDNA is transcribed into rRNA
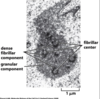
What type of chromosome has stalk and satellite DNA?
Acrocentric chromosomes
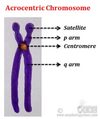
Where in the nucleus are acrocentric chromosomes located and what do they contain?
What human chromosomes are acrocentric chromosomes located on?
- Fibrillar regions
- rDNA
- 13, 14, 15, 21, and 22
Know the checkpoints of the cell cycle

T/F: rRNA is translated to protein
False
What is the length of helical DNA?
2 nm
How many genes are in a nuclear genome compared to mitochondrial DNA?
- Nuclear genome (>25,000 genes) – linear dsDNA
- Mitochondrial DNA (~35 genes) – circular dsDNA
What is the histone fold?
A common motif made up of 3 alpha helices and 2 loops that allows histone dimerization
What’s the process of histones becoming an octomer?
- H3-H4 dimerize –> 2 dimers = tetramer
- H3-H4 tetramer –> bind 2 H2AB dimers –> octomer
What is the overal process for preventing DNA replication at the origin of replication?
- Origin recognition complex (ORC) binds to origin of replication
- Degradation of phosphate
- ORC is phosphorylated to begin replication again

Know the step by step process for replication

What direction does synthesis occur?
5’ –> 3’
What direction do the leading and lagging strand grow in relation to the replication fork?
Leading strand: towards the fork
Lagging strand: away the fork
T/F: The leading strand has Okazaki fragments
False: the lagging strand has Okazaki fragments







