Exam 1: Flashcards
(124 cards)
3 neuronal shapes
multipolar, bipolar, unipolar
multipolar neurons
majority in vertebrates
multiple dendritic projections
bipolar neuron example
olfactory receptor neuron
unipolar neurons
common in vertebrates
DRG neurons are an example
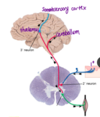
4 neuron classifications based on connections
sensory neurons
motor neurons
interneurons
projection neurons
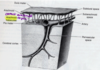
grey vs white matter
grey: cell bodies and dendrites
white: axons
dendritic spines
receive excitatory input
Sites of synaptic contracts (4)
AD: axodendritic (axon synapse on dendrite)
AS: axosomatic
DD: dendrodendritic
AA: axoaxonic
astrocytes: role and types
structural/metabolic support, injury response
types: protoplasmic (found in grey matter), fibrous (white matter), radial glia (during development, guide growing axons)
Ependymal cells
line brain ventricles
produce CSF
peak risk for birth defects is at how many weeks
3-5 weeks
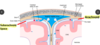
day 18:
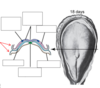
bilaminar disc formation (before neurulation
blastocyst (epiblast/hypoblasm) attach to uterine wall
epiblasm forms primitive streak, which eventually forms mesoderm
gastrulation
epiblasm cells migrate through primitive streak
endoderm cells displace hypoblasm
mesoderm forms b/w endoderm and ectoderm

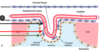
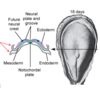
week 3 marks ____
beginning of primary neurulation
what happens during week 3
neural plate forms from ectoderm, separates
notochord forms from mesoderm, separates
neural crest cells forms from edge of ectoderm, separates

when is primary neurulation completed
week 4
week 4: 3 vesicles
prosencephalon, mesencephalon, rhombencephalon
week 4
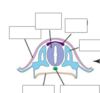

what happens during week 4
ectoderm begins to fuse into single layer
neural crest cells separate
neural tube begins to fuse (rostral end closes first)
3 primary vesicles form
somites form (future vertebrae)

secondary neurulation completed by:
week 7
total fusion
what happens during secondary neurulation
medullary cord exists as mass of cells in tail bud
caudal pore fuses, forming secondary cavity and medullary cord
secondary cavity extends into medullary cord and forms secondary neural tube

two major signaling molecules in neural tube development
bone morphogenetic proteins: produced by ectoderm
sonic hedgehog: produced by notochord