Exam 1 Histology Flashcards
(155 cards)
The primitive streak forms in the embryonic disc during prenatal development, causing:
a. initiation of palatal development.
b. bilateral symmetry.
c. fusion of the mandibular processes.
d. disintegration of the oropharyngeal membrane.
b. bilateral symmetry.
* During the beginning of the third week of prenatal development within the embryonic period, the primitive streak forms within the bilaminar disc. The primitive streak causes the disc to have bilateral symmetry,*
* with a right half and left half.*
What is cleavage and when does it occur?
Cleavage – the process during prenatal development when mitosis converts a zygote to a blastocyst
After fertilization, the zygote then undergoes mitosis, or individual cell division, that splits it into more and more cells due to cleavage. After initial cleavage, the solid ball of cells becomes a morula. Because of the ongoing process of mitosis and secretion of fluid by the cells within the morula, the zygote now becomes a blastocyst (or blastula). The rest of the first week is characterized by further mitotic cleavage, in which the blastocyst splits into smaller and more numerous cells as it undergoes successive cell division by mitosis.

When does the maxillary and nasal processes form?
4th week
The migratory cells located in the middle between the epiblast and hypoblast layers become mesoderm, an embryonic connective tissue, as well as embryonic ______.
endoderm
Neuroectoderm
specialized group of cells that differentiates from ectoderm. Gives rise to the respiratory epithelium and cells of glands

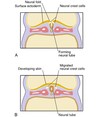
The neural crest cells migrate from the crests of the neural folds and then join the _______ to form mesenchyme.
mesoderm
By the end of the ______ week, the mesoderm additionally differentiates and begins to divide on each side of the tube into 38 paired cuboidal segments of mesoderm, forming the _____.
third; somites
Hypoblast
inferior layer from the bilaminar embryonic disc composed of small cuboidal cells.
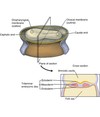
After a morula cleaves through additional mitotic divisions it is now called a __________
blastocyst
How many processes are included in facial development?
Facial development depends on the five major facial processes that form during the fourth week and surround the primitive mouth of the embryo:
1. frontonasal process.
2/3. mandibular process (paired)
4/5. maxillary process (paired)
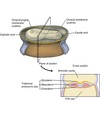
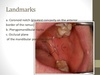
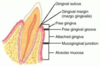
- The line of demarcation between the attached gingiva and the alveolar mucosa is the:
a. mucogingival junction.
b. interdental gingiva.
c. mucobuccal fold.
d. marginal gingiva.
a.mucogingival junction.
Junctional epithelium
the epithelial attachment provides a seal at the base of the sulcus
non keratinized separates the periodontal ligament from the oral environment

- The development of the neck parallels the development of the face over time, beginning during the fourth week of prenatal development within the embryonic period and completed during the _____ period.
a. preimplantation
b. embryonic
c. fetal
d. both the embryonic and fetal
c.fetal
______ is the superior layer of the bilaminar embryonic disc
Epiblast
Where do the neural crest cells migrate from?
These cells migrate from the crests of the neural folds and then join the mesoderm to form mesenchyme.
The line of demarcation between the firmer and pinker attached gingiva and the movable and redder alveolar mucosa is the scallopp-shaped ________
Mucogingival junction
There are 4 muscles of mastication:
- Masseter
- Temporalis
- Medial pterygoid
- Lateral pterygoid
All attach to the mandible and are innervated by V3
Form in the tenth week of development
First arches (mandibular arches)
Which of the following muscles is involved in the lateral deviation of the mandible?
a. masseter muscle
b. medial pterygoid muscle
c. lateral pterygoid muscle
d. temporalis muscle
e. digastric muscle
c. lateral pterygoid muscle
What are the 3 stages of pregnancy?
Preimplantation period – first week (zygote, blastocyst)
Embryonic period – weeks 2-8 (disc, embryo, folded embryo)
Fetal period – months 3-9 (embryo, fetus)
- In which week of prenatal development does facial development begin in the embryo?
a. Second
b. Fourth
c. Fifth
d. Eighth
b.Fourth
The ______ of the hyoid arches helps form the muscles of facial expression, the middle ear muscles, and a suprahyoid muscle.
mesoderm
in week 3 (embryonic period), the Neural Crest Cells develop into what?
- ) components of nervous system pigment cells, connective tissue proper, cartilage, bone, certain dental tissue
- ) Histologic Features- Varies
- ) Origin- Migrating neuroectoderm
- What does the maxillary process form from during the fourth week of prenatal development?
a. Lateral nasal processes
b. Mandibular arch
c. Intermaxillary segment
d. Medial nasal processes
b.Mandibular arch
What exact cells or structures develop from neuroectoderm and migrate from the neural folds to then join mesoderm to form mesenchyme during the third week of prenatal development?
a. Somites
b. Neural crest cells
c. Mesoderm
d. Yolk sac
b.Neural crest cells