Exam 1: Neurotransmitters Flashcards
(27 cards)
Neuronal synapses vary by
Size of synaptic contact
Neurotransmitter released
Efficiency of synaptic transmission
Mechanisms to terminate neurotransmitters
Synaptic plasticity (actively changing the effectiveness of the neuron or synapse itself)
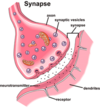
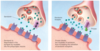
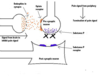
What does this image illustrate (in broad terms)

That recepters can be highly specidic (ACh on left image) or be activated by many neurotransmitters (image on right)
Know the main Classes of Synaptic Transmitters:
Classes of Synaptic Transmitters:
Amino acids
Monoamines
Cathecholamines
Neuropeptides
Know which transmitters Excite, Inhibit, or Modulate synapses:
***One of these will prob be on the exam***
transmitters that** **Excite synapses: (opens Na+ channels)
Glutamate, Aspartate, ACh*
transmitters that Inhibit** **synapses: (opens Cl- or K+ channels)
GABA, Glycine, ACh*, Serotonin, Dopamine*, Enkephalines*, Endorphins*
transmitters that Modulate synapses:
NE
*transmitters that sometimes activate these synapses
Name 4 Amino acids synaptic transmitters
Do they excite, inhibit, or modulate synapses?
Glutamate (excite; activates as Na+ channels)
Aspartate (excite; activates as Na+ channels)
GABA (inhibit; activates Cl- channels)
Glycine (inhibit; activates Cl- channels)

Glycine:
Secreted at _____ of the spinal cord
Is it Excititory, Inhibitory, or Modulatory?
Binds to its receptor which makes the _____ membrane more permeable to _____ ions; _____ the membrane
Participates in the processing of _____ and _____ information that permits _____, _____, and _____
_____ is a glycine antagonist
Glycine:
Secreted at synapses of the spinal cord
Inhibitory
Binds to its receptor which makes the postsynaptic membrane more permeable to chloride ions; hyperpolarizes the membrane
Participates in the processing of motor and sensory information that permits movement, vision, and audition
Strychnine is a glycine antagonist

Gaba: (Gamma-aminobutyric acid)
Secreted by _____ _____ in the spinal cord, cerebellum, basal ganglia, many areas of the cortex
Is it Excititory, Inhibitory, or Modulatory?
Receptor connected to _____ ion channel like glycine
_____ the membrane
_____ inhibits GABA release
_____ enhances GABA’s inhibitory effects
Gaba:
Secreted by nerve terminals in the spinal cord, cerebellum, basal ganglia, many areas of the cortex
MAJOR Inhibitory NT
Receptor connected to chloride ion channel like glycine
Hyperpolarizes the membrane
Caffeine inhibits GABA release
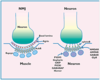
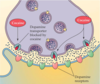
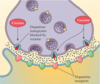
Pentobarbital enhances GABA’s inhibitory effects (greater potential change; see image)

Pentobarbital:
enhances _____ _____ effects
Pentobarbital:
enhances GABA’s inhibitory effects
Glutamate:
Secreted in many _____ pathways and in the _____ _____
Is it Excititory, Inhibitory, or Modulatory?
Ionotropic receptors _____ and _____
Glutamate:
Secreted in many sensory pathways and in the cerebral cortex
Excitation
Ionotropic receptors AMPA* and NMDA*
both excite, conduct of Na+
* some systems only have AMPA, some have BOTH. But NMDA requires AMPA (to the change membrane potential enough) to remove the Mg2+ blocking the NMDA recepter which allows it to open.

Name 3 Monoamine synaptic transmitters
Do they excite, inhibit, or modulate synapses?
ACh (normally excites, but some inhibitory)
Serotonin (inhibits)
Histamine
Acetylcholine:
Is it Excititory, Inhibitory, or Modulatory?
One of the characteristics of Alzheimer’s disease disease is marked decrease in Ach concentrations of the _____ _____ and _____ _____
Acetylcholine:
Excitation but… Some inhibitory effects*
*Peripheral parasympathetic nerve endings, and Inhibition of the heart by vagus nerve
One of the characteristics of Alzheimer’s disease is marked decrease in Ach concentrations of the cerebral cortex and caudate nucleus
Alzheimer’s:
A disease in which a marked deterioration occurs in the _____, the hallmark of which is _____ dementia.
One of the characteristics of this disease is marked _____ in _____ concentrations of the _____ _____ and _____ _____
Administering _____ in Alzheimer’s patients
Alzheimer’s:
A disease in which a marked deterioration occurs in the CNS, the hallmark of which is progressive dementia.
One of the characteristics of this disease is marked decrease in Ach concentrations of the cerebral cortex and caudate nucleus
Administering anticholinesterase in Alzheimer’s patients
Serotonin:
Secreted by nuclei that originate in the _____ _____ of the brain stem
Is it Excititory, Inhibitory, or Modulatory?
_____ of _____ pathways in the cord
_____ action in higher regions of the nervous system to help control _____ and perhaps _____
_____ drugs, such as _____, interact with serotonin
Depression medication also target serotonin by blocking the _____ causing _____ action (example: _____)
Serotonin:
Secreted by nuclei that originate in the median raphe of the brain stem
Inhibition
Inhibitor of pain pathways in the cord
Inhibitor action in higher regions of the nervous system to help control mood and perhaps sleep
Hallucinogenic drugs, such as LSD, interact with serotonin
Depression medication also target serotonin by blocking the re-uptake causing prolonged action (example: Prozac)
Name 3 Cathecholamine synaptic transmitters
Do they excite, inhibit, or modulate synapses?
Dopamine (inhibits)
NE (modulatory! Not an excitor or inhibitor)
Epinephrine

Dopamine:
Secreted by _____ that originate in the _____ _____
Is it Excititory, Inhibitory, or Modulatory?
Degeneration of dopamine-containing cells produce motor disorders such as _____ _____
Cocaine _____ dopaminergic activity in the brain by _____ dopamine _____
Amphetamines _____ _____ but also _____ dopamine from most brain regions
Dopamine:
Secreted by neurons that originate in the substantia nigra
Inhibition NT
Degeneration of dopamine-containing cells produce motor disorders such as Parkinson disease (due to over excitation!)
Cocaine increases dopaminergic activity in the brain by inhibiting dopamine re-uptake
Amphetamines inhibit re-uptake but also release dopamine from most brain regions (uses 3 mechanisms!)
Cocaine:
increases _____ _____ in the brain by inhibiting _____ _____
Cocaine:
increases dopaminergic activity in the brain by inhibiting dopamine re-uptake
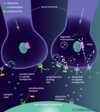
Amphetamine increases the concentration of dopamine in the synaptic cleft in 3 ways:
(1) It can bind to the _____ membrane of dopaminergic neurons and _____ the release of dopamine from the nerve terminal
(2) amphetamine can interact with dopamine containing _____ _____, releasing free dopamine into the nerve terminal
(3) amphetamine can bind to the dopamine _____ _____, causing it to _____ and transport free dopamine _____ the nerve terminal
Amphetamine increases the concentration of dopamine in the synaptic cleft in 3 ways:
(1) It can bind to the pre-synaptic membrane of dopaminergic neurons and induce the release of dopamine from the nerve terminal
(2) amphetamine can interact with dopamine containing synaptic vesicles, releasing free dopamine into the nerve terminal
(3) amphetamine can bind to the dopamine re-uptake transporter, causing it to act in reverse and transport free dopamine out of the nerve terminal
Norepinephrine:
Is it Excititory, Inhibitory, or Modulatory?
Norepinephrine:
Modulatory

Name a Purine Derivatives synaptic transmitter
Do they excite, inhibit, or modulate synapses?
ATP
It is not a sepecific excititory or inhibitory transmitter, but it does function as a NT
*Just know it can be a NT

Name a Neuropeptide synaptic transmitter
Do they excite, inhibit, or modulate synapses?
enkephalins (inhibits)
endorphines (inhibits)*
*same as enkephalins, but with a more potent and longer lasting effect

Enkephalins: (brief overview)
Is it Excititory, Inhibitory, or Modulatory?
Synthesis is increased during _____ _____
Enkephalins bind to the _____ receptors in the brain, _____ _____.
Enkephalins: (brief overview)
Inhibiting
Synthesis is increased during painful stress
Enkephalins bind to the opioid receptors in the brain, relieving pain.

Enkephalins: (mechanism)
Released _____ _____ synapses involved in transmitting _____ signals back to the brain, _____ _____ the terminal of a _____-signaling neuron
Enkephalins _____ the presynaptic membrane of the pain-signaling neuron, thus _____ it from transmitting _____ signals
_____ and other opioids bind _____ _____ _____ ( pain killers)
Enkephalins: (mechanism)
Released close to synapses involved in transmitting pain signals back to the brain, close to the terminal of a pain-signaling neuron
Enkephalins hyperpolarize the presynaptic membrane of the pain-signaling neuron, thus inhibiting it from transmitting pain signals
Morphine and other opioids bind these same receptors: (pain killers)

endorphines:
Is it Excititory, Inhibitory, or Modulatory?
same as _____, but with a _____ potent and _____ lasting effect
endorphines:
Inhibiting
same as enkephalins, but with a more potent and longer lasting effect
*Substance P is a type of endorphine
Nitric Oxide:
Secreted in areas of the brain responsible for _____-_____ behavior and _____
_____ than the other NT in its class
Not _____ and _____ in vesicles in the presynaptic terminal but is _____ _____ as needed and _____ to postsynaptic terminals
Nitric Oxide:
Secreted in areas of the brain responsible for long-term behavior and memory
Different than the other NT in its class
Not preformed and stored in vesicles in the presynaptic terminal but is synthesized instantly as needed and diffuses to postsynaptic terminals



