Exam 1 Spring Flashcards
(175 cards)
Quadrants and Regions of abdomen

Visceral Pain of abdomen
hollow organs: distention/forceful contraction
solid organs: stretching capsule
desc: gnawing, burning, cramping or aching
assoc: sweating pallor, nausea, vomit, restlessness
Parietal Pain of abdomen
orig: parietal pertoneum –> inflam
steady aching pain, more severe & precise localized than visc
worse with mvmt, cough
assoc with rebound tenderness
Rebound Tenderness
Blumberg’s Sign
Pain introduced or increased by quick withdrawal of pressure
Suggests peritoneal inflammation
“Which hurts more when I press or let go?

Referred Pain of abdomen
usually well localized
refer to chest, spine, pelvis
Vomitus
ask for:
- quant
- odor
- color
- bile: yellow-green
- blood: hematemesis:
- COFFEE GROUND : blood altered by gastric acids
- bright red
diarrhea
Increased water content of stool , stool volume >200 grams in 24 hours
Melena
Presence of black or tarry stool
upper GI bleed or from small bowel/right colon
Hematochezia
bright blood in stool
lower GI tract bleed or brisk upper GI bleed
Jaundice
Yellowish discoloration of the skin and sclera
From increased levels of bilirubin (a bile pigment derived mainly from the breakdown of hemoglobin)
Increased bilirubin is most suggestive of a hemoglobin problem (hemolysis) or a problem within the hepatobiliary system
Can range from benign (neonatal physiologic jaundice) to suggestive of life threatening disease (pancreatic cancer)
•Supra Pubic pain
–Can be caused by bladder or pelvic
–Bladder infection
–Urinary Retention
Order of the Physical Examination : abdomen
ØInspection
ØAuscultation
–Must precede percussion and palpation
ØPercussion
ØPalpation
ØSpecial tests
abdominal profiles


Abdominal Striae in Cushing’s Syndrome

Caput Medusae seen in Portal Hypertension

Sister Mary Joseph Nodule seen in Metastatic Disease

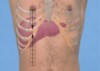
CULLEN’S SIGN
– Periumbilical ecchymosis
– Typically occurs in the presence of hemoperitoneum, hemorrhagic pancreatitis, or uterine tube rupture in ectopic pregnancy.
–Physical findings: Bluish discoloration or ecchymosis around the umbilicus; abdominal tenderness may also be present

GREY TURNER’S SIGN
–Flank ecchymosis
–Typically occurs in the presence of retro-peritoneal bleeding
–Hemorrhagic Pancreatitis
Auscultation of Bowel Sounds
Perform before palpation and percussion.. Why?
- Provides information about bowel motility
Use the diaphragm of your stethoscope
Note the frequency and the character of the bowel sounds
Types of Bowel Sounds: normal
- sounds occur 5 to 34 per minute in frequency and consist of gurgling and clicks in character
Types of Bowel Sounds: borborygmi
•are loud, easily audible sounds. Prolonged gurgles of hyperperistalsis. They are normal, too.
Types of Bowel Sounds: High pitched
•tinkling (raindrops in a barrel) sounds are a sign of early intestinal obstruction.
Types of Bowel Sounds: Increased
•diarrhea or early intestinal obstruction
Types of Bowel Sounds: Decreased
•(none for a minute) are a sign of decreased gut activity. Gut sounds may be markedly decreased after abdominal surgery; abdominal infection (peritonitis) or injury.