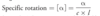Exam 2 Flashcards
(62 cards)
Angle strain
increase in energy associated w/ bond angle other than 109.5
torsional strain
difference in energy between staggered and eclipsed conformation
Cyclobutane
Angle strain bond angles of 88 degrees.
Slight torsional strain: Puckered conformation
Cyclopentane
Very little angle strain.
Slight torsional strain: Forms envelope conformation
ring flip
the conversion of one chair conformation into the other
1,3-diaxial interactions
steric ineractions between axial substituents in chair conformation
flagpole interactions
steric interactions between flagpole atoms in boat conformation
cis
same side of ring
trans
opposite side of ring
constitutional isomer
same formula but different connectivity of atoms
stereoisomesrs
same connectivity of atoms, different spatial arrangement
chiral
objects that are nonsuperimposable on their mirror images
chrial center
a carbon atom bearing four different groups
enantiomer
stereoisomers that are mirror images
diastereomer
stereoisomers that are not mirror images
R
clockwise
S
counterclockwise
polarimeter
device used to measure the ability of chiral organic compounds to rotate plane-polarized light
polarization
orientation of an electric field
plane-polarized light
light for which all photons have same polarization
optically active
- compound that rotates plane-polarized light
- chiral
optically inactive
- compound that does not rotate plane-polarized light
- achiral
observed rotation
- extent to which plane-polarized light is rotated by a solution of chiral compound
- depends on
- # of molecules light encounters
- path length
enantiomers rotate plane of light to _________ but ________
equal degrees, opposite directions