Exam #2 | Terminology Flashcards
(40 cards)
Animism
Animism encompasses the belief that objects, sacred places, animals and natural phenomena possess a distinct spiritual essence.
Such beliefs continue to be a crucial force in the religious lives of Southeast Asians and provide significant inspiration for various art forms within the region.
Ashlar Masonry
Fiinely dressed (cut, worked) stone, either an individual stone that was worked until squared or the structure built from it.
Ashlar is the finest stone masonry unit, generally rectangular cuboid, mentioned by Vitruvius as opus isodomum, or less frequently trapezoidal.

barrel vault
A barrel vault, also known as a tunnel vault or a wagon vault, is an architectural element formed by the extrusion of a single curve along a given distance.
The curves are typically circular in shape, lending a semi-cylindrical appearance to the total design.
A pair of curves would form a pointed barrel vault.

Bauhaus
Movement that championed a geometric, abstract style featuring little sentiment or emotion and no historical nods.
Its aesthetic continues to influence architects, designers and artists.
Bauhaus was an influential art and design movement that began in 1919 in Weimar, Germany

Buttress
Buttress, in architecture, exterior support, usually of masonry, projecting from the face of a wall and serving either to strengthen it or to resist the side thrust created by the load on an arch or a roof.

Flying buttress
Flying buttress, masonry structure typically consisting of an inclined bar carried on a half arch that extends (“flies”) from the upper part of a wall to a pier some distance away and carries the thrust of a roof or vault.

cantilever
Cantilever, beam supported at one end and carrying a load at the other end or distributed along the unsupported portion.
The upper half of the thickness of such a beam is subjected to tensile stress, tending to elongate the fibres, the lower half to compressive stress, tending to crush them.

Corinthian order
This architectural style is characterized by slender fluted columns and elaborate capitals decorated with acanthus leaves and scrolls.
The Corinthian order is the last developed of the three principal classical orders of ancient Greek and Roman architecture.

Deconstruction
Deconstruction is a form of criticism first used by French philosopher Jacques Derrida in the 1970s which asserts that there is not one single intrinsic meaning to be found in a work, but rather many, and often these can be conflicting.
Digital Imaging
Digital art is work made with digital technology or presented on digital technology.
This includes images done completely on computer or hand-drawn images scanned into a computer and finished using a software program like Adobe Illustrator.
Doric order
The Doric order is characterized by a plain, unadorned column capital and a column that rests directly on the stylobate of the temple without a base.
The Doric entablature includes a frieze composed of trigylphs—vertical plaques with three divisions—and metopes—square spaces for either painted or sculpted decoration.

Facade
In architecture, the “face” of a building.
Especially applicable to the principal front that looks onto a street or open space.
groin vault
A vault produced by the intersection at right angles of two barrel vaults.
Sometimes the arches of groin vaults may be pointed instead of round.

Guilds
An association of artisans and merchants who oversee the practice of their craft/trade in a particular area.
Iconoclasm
1: Attacking settled beliefs or institutions.
2: Opposing the veneration of religious images.
iconography
An iconography is a particular range or system of types of image used by an artist or artists to convey particular meanings.
For example in Christian religious painting there is an iconography of images such as the lamb which represents Christ, or the dove which represents the Holy Spirit.
intaglio
Intaglio describes any printmaking technique in which the image is produced by incising into the printing plate.
The incised line or area holds the ink and creates the image.
Sub-Forms can include:
* Etching
* Drypoint
* Engraving
* Wood Engraving
International / Modern
Style Architecture
The term international style was first used in 1932 to describe architects associated with the modern movement whose designs shared similar visual qualities – being mostly rectilinear, undecorated, asymmetrical and white.

ionic order
Ionic columns normally stand on a base which separates the shaft of the column from the stylobate or platform while the cap is usually enriched with egg-and-dart.

Iwan
In Islamic architecture a vaulted space, walled on three sides, with a monumental portal opening onto a courtyard.

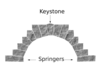
Keystone
The wedge-shaped stone at the apex of a masonry arch or typically round-shaped one at the apex of a vault.
For aesthetics, keystones are often larger than ribs in vaults and many of the voussoirs (arch stones) in arches, or embellished with a boss.
Kiva
A Hopi word used to refer to specialized round and rectangular rooms in modern Pueblos.
Modern kivas are used by men’s ceremonial associations. Archeologists assume that ancient kivas served similar functions.
Kivas are an important Southwestern architectural form.

Mana
The spiritual life force energy or healing power that permeates the universe, in the culture of the Melanesians and Polynesians.
Anyone or thing can have Mana. It is a cultivation or possession of energy and power, rather than being a source of power. It is an intentional force.
Metope
In classical architecture, a metope is a rectangular architectural element that fills the space between two triglyphs in a Doric frieze.
The frieze is a decorative band of alternating triglyphs and metopes above the architrave of a building of the Doric order.















