Exam 3 Flashcards
(233 cards)
vasc of uterus
uterine A, then ovarian A
caput medusae
dilated Cutaneous veins in anterior ab wall due to:
- portal htn
- SVC/IVC obstruction

ASIS (anterior superior iliac spine) lies at the level of
sacral promontory
innervations to bladdar
vesical/prostatic plexus
PNS (s2-s4): contract detrusor, relax internal urethral sphincter
SNS: relax detrusor, constrict internal sphincter
Mesentery proper
dbl fold peritoneum
suspends jejunum and ilieum from post ab wall
- The root extends diagonally from the duodenojejunal flexure to the right iliac fossa.
- Its free border encloses the small intestine.
- Contains the superior mesenteric and intestinal (jejunal and ileal) vessels, nerves, and lymphatics.
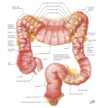
Transverse colon
R hepatic flexure –> L splenic flexure
largest and most mobile
txverse mesocolon attachment to posterior ab wall
N: superior & inferior mesenteric plexus
A: SMA - R, L, middle colic
V: SMV - R, L, middle colic
L: middle colic
lymph of duodenum
follow A
–pancreaticoduodenal, pyloric, superior mesenteric, and celiac lymph nodes
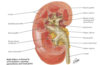
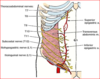
Peri-nephric abscess
spread to pelvis due to fascial attachment
- DOES NOT SPREAD TO ADJ KIDNEY
causes:
- UTI
- staph aureus
- DM
- lsions of urinary tract: stones, cyst
Intraperitoneal Injection
•widely used to administer chemotherapy drugs to treat some cancers, particularly ovarian cancer.
Fluid injected into the peritoneal cavity is absorbed rapidly
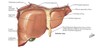
functional “left liver” inclues
L lobe, caudate, quadrate lobes
Inguinal ligament

lower free border of external oblique
folds backwards on self
ASIS –> pubic tubercle
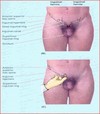
direct inguinal hernia
WEAK posterior wall of inguinal canal
No descent into scrotum
medial to inferior epigastric vessels
aquired
Older age
basic celiac trunk pic

Lymphatic drainage of female reproductive organs
- ovary, uterine tube, and fundus follow the ovarian artery and drain into the paraaortic nodes/ lateral/ pre/ lumbar.
- uterine body and cervix drain into the internal and external iliac nodes
2nd part duodenum
descending R of L1–L3
–major duodenal papilla on posteromedial wall = opening of hepatopancreatic ampulla
Thoracic esophagus
superior mediastium, L of median line
- pass behind and R of aortic arch
- desc posterior mediastinum along the right side of the descending aorta
diagphragm @ T10
- distinct dilation before entering diaphragm
front: trachea, aortic arch, R pulm A, L bronchus, pericardium
behind: v-colum, longus colli M, R aortic intercostal, thoracic duct, hemiazygos V
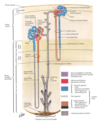
Venous drainage of prostate
prostatic venous plexus b/w true and false capsules
connect to Batson plexus (valve less)
•Veins of most of the pelvic organs are connect to Batson plexus ( except for ovaries and testis)
- how pelvic cancer can spread to the vertebral column
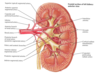
venous drainage of kidney
R & L renal V
- anterior to A
- L receives L suprarenal and L gonadal
drain to IVC
L passes anterior to aorta, posterior to desc SMA
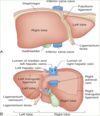
NAVL of liver
N: hepatic N plexus: SNS from celiac plexus, PNS from vagus
A: portal vein (70%), hepatic (30%)
V: 3 formed by union of central veins –> drain to IVC inferior to diaphragm
L: hepatic –> celiac –> cisterna chyli
Subphrenic (Suprahepatic) Recess
pocket b/w diaphragm and anterior/superior part of liver
separated into right and left recesses by the falciform ligament.
innervation to large intestine
PNS - vagus, pelvic splachnic
SNS: T10-L2
N, A, V, L of scrotum
N:
- anterior 1/3 = ilioinguinal, genitofemoral - genital branch
- posterior 2/3 = pudendal, posterior cut N of thigh
A:
- pudendal –> scrotum
- inferior epigastric –> cremastric
V:
- same as A
L:
- superficial inguinal
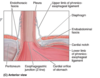
Rectus sheath
•Aponeurosis of int. obl. splits to enclose rectus abdominis to form rectus sheath
anterior
- above arcuate line
- Aponeurosis of external and internal oblique
- Below arcuate line
- Aponeurosis of external oblique, internal oblique and transverse abdominis
posterior
- •Above arcuate line
- •Aponeurosis of internal oblique and transverse abdominis
- •Below arcuate line
- •Deficient, rectus abdominis lie on fascia transversalis
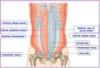
Nerve supply to stomach
PNS
- From anterior and posterior vagal trunks.
- Increase peristalsis and relax pyloric sphincter.
SNS
- From T6–T9 spinal cord segments via great splanchnic nerve to celiac plexus.
- Inhibit peristalsis and contract pyloric sphincter.