exam Flashcards
(69 cards)
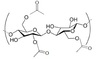
Polyester
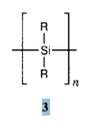
Polyether

Polyimide

Glass Transition Temperature (Tg)
The temperature (actually a broad range of temperatures) at which a glassy polymer softens into a viscous liquid or rubbery phase.
On the molecular level, it is the temperature at which chains in amorphous (i.e., disordered) regions of the polymer gain enough thermal energy to begin sliding past one another at a noticable rate.
Polydispersity Index (PDI)
The ratio of Mw to Mn is known as the polydispersity index (PDI), and provides a rough indication of the breadth of the distribution.
Mw/Mn
M0
Monomer Concentration at time = 0
Mt
Monomer concentration at time = t
P
% conversion of monomer to polymer
Xn
DP=Degree of polymerization
Distinctions between step growth and chain growth (component reactions)
- Step Growth
- I, P, T identical in rate and mechanism
- Chain Growth
- I, P, T are distinct steps with different rates and mechanisms
Distinctions between step growth and chain growth (Polymer Growth)
- Step growth
- Coupling can occur between any 2 species (monomer, oligomer or polymer) - all very reactive
- Slow, random growth of MW, very high conv. req. before AnY polymer chains are formed
- All species reactive throughout polyimerization
- Chain growth
- Occurs by random addition of M to a very small number of active chains
- Rapid increase in molecular weight, high polymer forms immediatel
- Only very few chains grow at any point in time. Mostly monomer and inactive chains
Distinctions between step growth and chain growth ( monomer concentration)
- Step growth
- [M] decreases rapidly before any HMW polymer forms
- Compared with chain final, Xn small, Mn~40-60k
- Chain growth
- [M] decreases slowly
- Xn, Mn very high
- Mn ~105-106
Distinctions between step growth and chain growth (Rate of Polymerization)
- Step growth
- Maximum at start of polymerization, decreases as pzn proceeds
- Chain growth
- Initially Rp=0, quickly rises to a maximum, then remains ~constant, then decr.
Distinctions betwen step growth and chain growth (heat of polymerization, reaction mixture)
- Step growth
- Not very exothermic, some endothermic, most are heated
- At any tiem t, all molecular species present in calculable distribution
- Chain growth
- Very exothermic
- Only M and high polymer, and ~10-8 mol/L growing chains
Polymerization kinetics summary
- Step growth (condensation)
- Deviation form linearity at high conversion (slows)
- Nylon, PET produced commercially this way
- Rate dependant on [M]3
- Free radical chain growth
- Autoacceleration at high conversion and high [M] (faster)
- Most polymers produced commercially this way (e.g. PS)
- Rate dependant on [M] and [I]1/2
- Living chain growth (e.g. anionic)
- No termination or chain transfer
- Block and end-functional polymers possible
- Rate dependent on [M], when Kp>>>Ki
Polymers are viscoelastic

Stress-strain curve

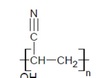
Polyacrylonitrile (PAN)
Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVOH)

Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
PVC

Polyethylene Glycol (PEG)

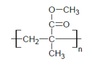
Polymethyl methcrylate (PMMA)
Nylon 6.6 (Nylon 6.6)

Polycarbonate (PC)