Exam II Flashcards
(175 cards)
Hormones of the anterior pituitary
Adrenocortocptropic hormone (ACTH)
Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH)
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Growth hormone (GH)
Prolactin Beta-Lipotropin (fat catabolism)
Beta-endorphins (pain perception)
Hormones of the posterior pituitary
Synthesized in the nuclei of the hypothalamus
Stored and secreted by the posterior pituitary
- Antidiuretic hormone (ADH, arginine vasopressin)
- Oxytocin
ADH
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH, arginine vasopressin)
Controls plasma osmolality
Causes water reabsorption into the blood
Is released when plasma osmolality is increased or intravascular volume is decreased
Hormones of the Hypothalamus
Prolactin-inhibiting factor (PIF)
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH)
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
Somatostatin
Growth hormone-releasing factor (GRF)
Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH)
Substance P
Other name for Anterior pituitary
adenohypophysis
Other name for Posterior pituitary
neurohypophysis
Examples of Steroids (Lipid-Soluble) Hormones
Androgens, estrogens, progestins, glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, vitamin D, retinoid
What do steroids activate?
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) polymerase
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) transcription
General characteristics of hormones
Specific rates and rhythms of secretion
Operate within feedback systems
Affect only cells with appropriate receptors
Are inactivated by the liver or directly excreted by the kidneys
What is up-regulation of hormones?
Low concentrations of hormones increase the number of receptors per cell
What is down-regulation of hormones?
High concentrations of hormones decrease the number of receptors
The five steps of bone repair
Hematoma formation
Procallus formation
Callus formation
Replacement
Remodeling
Synarthrosis
Immovable
Typically fibrous Joints
Examples: Sutures, syndesmoses, and gomphoses
Amphiarthrosis
Slight movement
Typically cartilaginous joints
Symphysis
Synchondrosis
Symphysis
Bones are united by a pad or disk of fibrocartilage
Synchondrosis
Bones are united by hyaline cartilage (costal cartilage)
• Examples: Joints between the ribs and the sternum
Diarthrosis
Move freely
Typically synovial joints
Five classifications of bone fractures
- Complete
- Incomplete
- Comminuted
- Linear
- Oblique
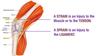
What is a sTrain?
Injury to a Tendon
o Tear or injury to a tendon (fibrous connective tissue that attaches skeletal muscle to bone)

What is a sPrain?
Injury to a ligament
o Tear or injury to a ligament (fibrous connective tissue that connects bones)
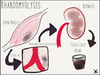
What is rhabdomyolysis?
Breakdown of muscle
Protein pigment myoglobin enters extracellular space, then to the blood stream and eventually to the kidneys
Crush syndrome
Rhabdomyolysis
o Can cause kidneys to shut down
o Can be life threatening
How do you treat Rhabdomyolysis?
- Rapid intravenous hydration
- If hyperkalemic, may require hemodialysis
Treatment of RA
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) such as methotrexate (MTX, first line), azathioprine, sulfasalazine, hydroxychloroquine, leflunomide, and cyclosporine<
- Biological DMARDs (bDMARDs): Medications affect specific processes in the development of RA, such as TNF
- NSAIDs, glucocorticoids, intraarticular steroid injections
- Physical and occupational therapy with therapeutic exercise and use of assistive devices
- Surgery: Synovectomy or joint replacement



