Exam II Osteology Flashcards
(67 cards)
Pectoral girdle consists of:
Scapula
Clavicle
Brachium consists of:
Humerus
Antebrachium consists of:
Radius
Ulna
Palpable parts of the scapula
- Spine
- Acromion
- Medial border
- Inferior border
- Coracoid process
Palpable areas of the clavicle:
- Superior border
Palpable parts of the humerus:
- Medial and Lateral epicondyle
- Greater and Lesser tuburcle
Palpable parts of the radius:
(thumb side)
- Head
- Styloid process
Palpable parts of the ulna:
(pinky side)
- Head
- Styloid process
- Posterior border
What joint deals with shoulder displacement?
Gelnohumeral joint; Shoulder joint
What join is involved with complete shoulder separation?
Acromioclavicular joint


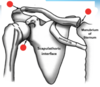
Label Joints















Muscle Attachment sites of the os coxae
Inferior Gluteal line
Anterior Gluteal line
Posterior Gluteal line
Palpable sites of the os coxae
Iliac crest
PSIS - posterior superior iliac spine (dimple)
Ischial tuberosity
Muscle attachment site(s) in the sacrum
Lateral sacral crest
Palpable sites of the posterior and anterior sacrum
Median sacral crest
Coccyx
Muscle attachment site(s) of the femur
Greater trochanter

















































