facts Flashcards
(543 cards)
why/ when to give potassium along with IV insulin
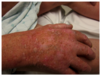
hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (exacerbation of DM) glucose < 600 with normal electrolytes and serum osmolality > 350 have to give potassium if < 5.3 bc even though lab K is normal, its actually low bc of urinary K release (inc glucose= osmotic diuresis)
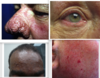
sore throat, cough worse at night, morning hoarseness, inc need for albuterol inhaler after meals dx?
in this dx - what would be alarm sx (6) and how do they change management approach
GERD (often associated w asthma bc micro-aspiration of gastric contents w GERD leads to inc vagal tone and bronchial reactivity = asthma)
alarm sx= get endoscopy!!
- weight loss, hematemesis, melena, persistant vomiting, dysphagia, anemia

osteoporosis risk factors (6)
old age low weight postmenopausal smoking excessive alc intake sedentary lifestyle
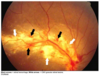
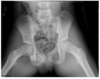
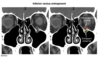
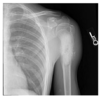
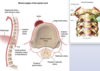
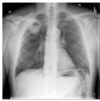
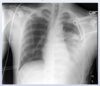
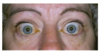
pointing at what, what is this called
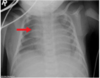
thymus: sail sign
effect of hyperALD on system pH
tPa- what is the actual medication
IV altepase
what is kleptomania
impulse control disorder starts in adolescence, the impulse to steal little things. instant relief when they do it followed by guilt or shame.
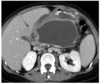
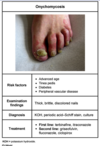
gallstone pancreatitis
in addition to pancreatitis signs, what suggests specfically gallstones pancreatitis and how do you diagnose
in addition to epigastric pain that shoots to the back and inc amylase:
inc BMI, ALT>150, inc Alk Phose suggest GB Pancreatitis
get a RUQ US to confirm
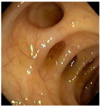
what is the gold standard for diagnosing celiac’s and why that specifically?
colon biopsy revealing villous atrophy
anti-TTG ab might actually be negative because celiac ds is associated with IgA deficiency. so a negative anti-TTG ab does not rule out celiac
precocious puberty vs premature thelarche/adrenarche
bone age

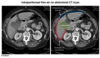
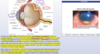
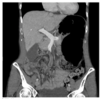
what is the histopathological change seen in diabetic nephropathy

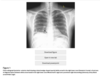
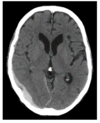
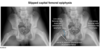
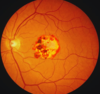
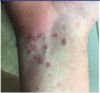
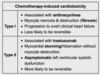
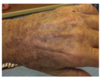
what is the finding
what disease is this finding associated with

thymoma (an anterior mediastinal mass)
-Myasthenia Gravis: will present with dysphagia and unable to swallow = bulbar dysfunction
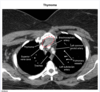
what is the pathiphysiology of myasthenia gravis
autoAb from the thymus against n-Ach R in the neuromuscular junction –> impaired action potential at receptors –> M wkness
will have weakness that is worse throughout the day, often presents with fatiguable chewing or dysphagia
treatment for:
- asx gallstones
- gallstones with biliary colic
- acute gallstones w cholecystitis, hemodynamically stable patient
within 72 hours dec mortality and length of hospital stay compared to delayed surgery

dx + treatment of toxic megacolon
dx= colonic dilation > 6cm on CT, loss of haustra
trx= if pt is stable, can do IV fluids, bowel rest, nasogastric decompression, broad spectrum Ab
TM secondary to UC–> IV glucocorticoids is first line therapy
MC cause of viral gastroenteritis
norovirus
presents w non-bloody non-bilious V, abd pain, and waterry diarrhea
develops 2-3 days after the event (school event, cruise..)
what is the time frame needed for a diagnosis of major depressive disorder
2 weeks

what are the sx of organophosphate poisoning
what is the treatment

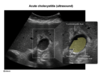
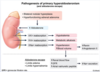
risk factors and organisms that cause emphysematous cholecystitis
- DM, vascular compromise, immunosuppression
- C. dif, E. coli

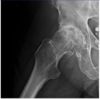
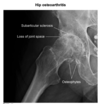
5 big risk factors for avascular necrosis
- femoral head fracture
- glucocorticoids
- excessive alc use
- SLE
- sickle cell
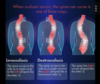
how does acetazolamide effect the renal tubule?
which diuretics can cause hypokalemia?
which diuretics are K-sparing?
which diuretics can cause metabolic acidosis?
- acetozolamide= prevent proximal reabsorption of bicarb
- hypokalemia = thiazide diuretics
- K sparing= spironolactone/eplerenon, amiloride
- can cause metabolic acidosis= amiloride (dec gradient for H+)
- amiloride = direct inhibit ENaC: can also cause hyperkalemia
- vs spironolactone= x ALD receptor= indirect ENaC inhibit: spare K but no cause met acid
–if develop hyperK –> switch to another BP agent i.e. CCB amlodipine

primary sclerosing cholangitis
- lab markers
- complications/inc risk for what else
PSC
- inc alk phos (+bilirubin), inc GGT
- 90% pts have IBD –> need to get colonoscopy to rule it out if you have PSC
- inc risk for colon CA, cholangiocarcinoma, biliary CA
- inc risk for biliary strictures, cholelithiasis, cholestasis –> dec ADEK, osteoporosis
- preferred INR range for warfarin in setting of a fib.
- going into surgery/in hemorrhage, how do you adjust the INR
- preferred for a fib: btwn 2-3
- bring INR back to ~1= give prethrombin complex concentrate (factors 2,9,7,10,protein c&s) + IV vitamin K
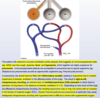
how do you calculate the “number needed to treat” to have X effect
NNT= 1/(absolute risk reduction)
ARR= (risk of control) - (risk of experimental group)
(i.e. 24% placebos got asthma, 17% treated got asthma –> ARR= 24-17 = 7.2 % –> NNT= 1/0.072 = 14)