Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring Flashcards
(84 cards)
when are late decels considered “ominous”?
when are they considered severe?
- ominous if accompanied with lack of variability
- severe if decreased more than 45 bpm
what is minimal vs. marked FHR variability?
(book)
- minimal - amplitude range of 5 bpm or less
- marked - amplitude range of > 25 bpm
what type(s) of decels require urgent assessment of fetal status
late and variable
early decels and risks of hypoxia?
no risk of fetal hypoxia
what do antepartum accelerations correlate with?
- fetal movement
- accelerations = happy bebe
- book: ensures absence of fetal acidosis or hypoxemia, providing reliable reassurance of fetal well-being
how do CNS depressants given to mom generally impact the bebe?
(book)
decreased FHR variability
what three categories qualify a patient as a high-risk pregnancy?
- medical complications
- fetal complications
- intrapartum complications
what it this and what can cause it

early decel
head compression
what two factors have an impact on the intrinsic fetal heart rate
- neuronal
- humoral
normal baseline FHR
what is baseline FHR? (book)
110-160 bpm
baseline FHR is determined as the mean FHR rounded to 5bpm during a 10-minute period that has no accelerations, decels, or marked variability
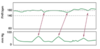
what type of variability is seen in this shitty picture from the book

marked
what do late decels usually indicate?
(book)
uteroplacetal insufficiency
causes of prolonged decels
(book)
- uncorrected maternal hypotension
- maternal supine position
- uterine hyperstimulation
- prolapsed cord
- cord entanglement
- uterine rupture
- placental abruption
examples of fetal complications that indicate high risk pregnancy (6)
- IUGR
- nonlethal anomalies
- prematurity
- multiple gestations
- postdatism (?)
- hydrops
what device measures pressures inside the uterus?
intrauterine pressure catheter
what can variable decels indicate?
- vagal activity
- umbilical cord occlusion (partial or complete, or occlusion from short cord stretching)
what type of receptor responds to an increase in BP in the fetus?
what type responds to decreased PaO2 and increased PaCO2?
- BP - baroreceptors
- CO2 - chemoreceptors
what interventions will correct most cases of fetal bradycardia before an expedited c section is necessary?
(book)
prompt treatment of hypotension and uterine overactivity
what is a sinusoidal FHR pattern and what does it look like?
causes?
(book)
- cycle frequency of 3-5/minute and amplitude of 5-15 bpm which persists 20+ min
- smooth, sine, wave-like, undulating pattern (tbh looks like v tach)
- strongly predictive of fetal asphyxia
- also - fetal anemia, occasional maternal opioid use
what questions would you address when determining if an epidural is adequate for use in c-section?
- is it patchy?
- will the patient/fetus tolerate additional LA to achieve adequate level?
- how quickly can adequate level be achieved?
- what is the probability of block failure?
- would a SAB behoove the situation? would it make things worse?
how does an external FHR transducer use doppler ultrasound
what is an alternative to this?
detects changes in ventricular wall motion and blood flow through major vessels
alternative - scalp ECG lead to measure R-R interval
what can early decels indicate?
head compression
what is an acceleration and how long does it last?
- abrupt change in fetal heart rate above baseline
- Per book- >15 bpm if 32 weeks and 10 if < 32 weeks
- at least 15 beats above baseline for at least 15 seconds
what is a saltatory FHR pattern?
what can cause it?
what is it weakly associated with in the fetus?
- excessive alterations in variability
- caused by acute fetal hypoxia
- weak association to low Apgar scores