Final Flashcards
(321 cards)
Fed: Absorptive State: efect on metabolism
•Anabolic (but not gluconeogenesis):
- Synthesis:
- glycogen
- TG
- protein
- •Urea cycle (if high protein ingested)
liver metab: 2 hours after eating
insulin drops = gng increase
Xeropthalmia
dry eye syndrome
night blindness
xerosis: sclera = wrinkles, less shiny
- Bitot’s spots - Patches of little gray bubbles on the sclera
- Keratomalacia - Soft or bulging cornea. Opacities (keratin deposits)

Genetics of Obesity
30-40% = heredity
Familial aggregation: clustering of obesity in families
identical twins > non-identical twins
stress and insulin
stress —> + epi —> - insulin –> - dietary fuel
cobalt
fx: vit b12
defic sympt: anemia
•Korsakoff’s psychosis
- hallucinations
- Loss of memory
- Confabulation (making up stories)
B1
•During initial fasting what fuel does the brain use for aerobic metabolism?
•Glucose.
prefers glucose
under prolonged fasting will use Ketone Bodies as the prefered state
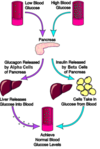
Islets of Langerhans
- α-cells (20%) produce glucagon
- β-cells (60-80%) produce insulin
- δ-cells (about 5%) produce somatostatin
allosteric regulation during fasting stages

initiator:of Insulin Secretion
- Glucose = most important
- aa
- GI hormones (Secretin)
What causes Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome
•Most common B1 deficiency in developed countries
chronic alcoholics
Impaired intestinal absorption
poor diets
increased demand with carb, etoh
mg2+ deficiency
Deficiency of Niacin
pellagra: 4 D’s
dirrhea, dermatitis, dementia, death
- derm: esp areas exposed to sunlight - thicken, scales, hyperkeratin
glossitis: swollen tongue
Vitamin D
synth from inactive precursors from diet:
- ergocalciferol: D2 - plant
- cholecalciferol: D3 - animal
•Can also be synthesized from 7-dehydrocholesterol in the skin of persons exposed to sunlight
RDA: 5mg cholecalciferol, 200 IU/day vit d
Insulin Also Signals via ______ Pathway
PI 3-Kinase
- insulin binds to tyr receptors
- irs
- PI-3 kinase
- PDK 1
- activated and disassociated from membrane
Sources and Functional Forms
of Water Soluble Vitamins
chart

HH type 1
HFE
recessive
parenchymal iron overload, cirrh
Pro-Oxidant
Fe2+
Cu2+
Cr3+
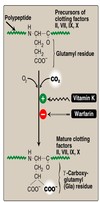
Vitamin K3
- insulin –> carboxyl-terminal tyr residues
- irs-1
- SH2 domain of Grb2 of irs, sos binds RAS: GDP –> GTP = bind to Ras
- raf-1
- mek
- erk = map kinase
Vitamin D Toxicity
- Most toxic of fat soluble vitamins
- Excess calcitriol –> hypercalcemia and hypercalciuria
- Dazed appearance
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea, thirst and stupor
- May present with sarcoidosis
- •Inflammation of tissues marked by clusters of immune cells (granulomas)
- •Affects lungs, skin and lymph nodes
Brain: Fed State: uses what as fuel?
glucose
Consumes 120g glucose/day
70% of the energy is used to maintain the Na+/ K+ membrane potentials
fluoride
bone and tooth strength
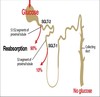
HbA1c
covalent bonded gluc on NH2 group of N-terminal val of beta-globin chain
slow glycation of HbA: dep on plasma [gluc]
- < 6.1 indicates good glycemic control
- reflects level of 6 wks prior to measurement
Melanocortin
•(α-MSH) is an anorexigenic (appetite-suppressing) signal
stim: leptin, insulin
overprod in Addison’s and CAH
decreased production in Cushings