Final Practical Exam Flashcards
(70 cards)
Crossover test for shoulder
Tests for AC Joint Pathology

Long head biceps TP
Location: bicipital groove
Position: Woe is me
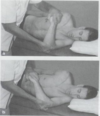
Anterior hip joint capsule stretch/mobilization
Remember to stand on the OPPOSITE side of the dysfunction

Innominate inflare/outflare treatment

Hip Drop Test
Test of the lumbar spine’s ability to side-bend. Not a test of the hip’s ability to drop
Patrick test
Indicates SI and hip dysfunction
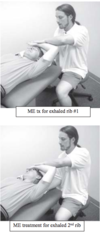
Treatment for superior clavicular head
Patient supine
Extend the arm off the side of the table and induce internal rotation
Patient flexes arm against resistance2-3 times
Reassess

McMurray’s Test
Test for damage to medial and lateral menisci
The side of the knee being gapped is the side being tested
Varus and valgus stress applied in opposite direction to rotation of tibia

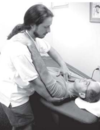
Spencer Technique
General: evaluates passive range of motion and used for treatment of adhesive capsulitis or restricted ROM form fibrosis, remember to stabilize the scapula and clavicle, all motions performed except external rotation
1) Extension
2) Flexion
3) Circumduction with compression
4) Circumduction with traction
5) Abduction
6) Internal rotation
7) Traction/Distraction

Piriformis TP
Belly of the piriformis

Talar tilt test
Inversion stress test to assess integrity of the calcaneo fibular ligament
Medial ankle TP
1” arc under the medial malleolus
Treats the tibialis anterior
Foot on pillow off table with bad leg up so you can push down
Induce inversion with slight internal rotation

Supraspinatus TP
Location: belly of supraspinatus
Position: 45 degrees of flexion/abduction/external rotation, otherwise jsut 180 degrees of abduction

Medial Meniscus TP
Located on medial joint line
Treated with leg off table, flex knee to 40 degrees, slight varus stress and internal rotation

Anterior trochanter TP
Sartorius Muscle
1-2 in caudad and slightly medial to ASIS
Talocalcaneal (Subtalar) Joint diagnosis
Testing for anteromedial and posterolateral glide of the calcaneus on the talus

Gluteus Medius TP

Scapular release MFR

Piriformis muscle energy

What abdominal medical problems can cause a positive Thomas test?
Kidney stones and pancreatitis
Shoulder impingement tests
Does not tell you the cause, but is a symptom
Most often caused by subacromial bursitis or supraspinatus tendinitis or a tear
Abduct arm to 180 degrees–impingement present ifshoulder will not abduct beyond 90 degrees without pain
Hawkin’s test: flex and internally rotate the shoulder while placing downward pressure on the wrist
Neer’s test: flex arm with internal rotation

Subdeltoid bursa TP
Location: under acromion high on anterolateral humerus, found best by abducting the arm
Position: Statue of liberty

Aprehension test for the shoulder
Tests for chronic anterior dislocation of the shoulder

Jobe’s sign/test
Test for supraspinatus tendinitis