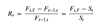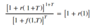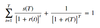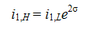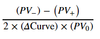Fixed Income Flashcards
(105 cards)
Convenience yield
Benefit of holding the physical commodity (not through a future)
Super classes of assets
- Capital assets
- Store of value assets
- Consumable or transferable assets (C/T)
- Futures contract size
- Tick
- Point value
- Smallest change in price
- Backwardation
- Contango
- Futures prices are lower than the spot price
- Futures prices are higher than the spot price
Total return on futures investments
= spot return + roll return + collateral return
Excess return
= spot return + roll return
Spot curve
Annualized return on a risk-free zero coupon bond with a single payment of principal at maturity
Forward price P(T* + T)
P(T* + T) = P(T*) F(T*, T)
- T* = number of years before the initiation of the contract
- T = tenor of the contract
- When the spot curve is upward sloping
- When the spot curve is downward sloping
- f(T*, T) > r(T* + T), r(T* + T) > r(T*)
- f(T*, T) < r(T* + T), r(T* + T) < r(T*)
Par curve
YTM on a risk-free coupon-paying bond priced at par
Fixed-rate leg of an interest swap
Swap rate
- Discount factor
- Rate associated with the previous discount factor
- 0.95/1.00 = 0.95
- [1/0.95] - 1 = 0.05263
- s(T)
- P(T)
- r(T)
- Swap rate a time T
- Discount factor with maturity T
- Spot rate at time T (YTM)
“On-the-run” government security
The most recently issued security
Gilts
UK government bonds
The Z-spread, ZSPRD
Spread over the default-free spot curve
/
The constant basis point spread that would need to be added to the implied spot yield curve so that the discounted cash flows of a bond are equal to its current market price
The Interpolated Spread - I-spread - ISPRD of a bond
Difference between its yield to maturity and the linearly interpolated yield for the same maturity on an appropriate reference yield curve
The pure expectations or unbiased expectations theory
The forward rate is an unbiased predictor of the future spot rate
Local expectations theory
A form of the pure expectations theory that suggests that the returns on bonds of different maturities will be the same over a short-term investment horizon
Liquidity preference theory
A premium exist for long-term securities
Segmented markets theory
The yield curve is influenced by the preferences of lenders and borrowers
The preferred habitat theory
Agents and institutions will accept additional risk in return for additional expected returns
Riding the yield curve
Buying bonds with maturities longer than the investment horizon
TED spread
Difference between the interest rates on interbank loans and on short-term U.S. government debt (“T-bills”). TED is an acronym formed from T-Bill and ED, the ticker symbol for the Eurodollar futures contract.