FunMed Pulmonary Flashcards
(235 cards)
Adult ICU CAP treatment
- ICU: B-lactam + macrolide OR B-lactam + fluoroquinolone
- broaden antibiotics with Pseudomonas coverage, i.e., B-lactam
- Consider further testing if not improving (eg CT of chest); thoracentesis if pleural fluid is present
- Outpatient: macrolide +/- B-lactam; doxycycline
- Inpatient: B-lactam + macrolide OR a respiratory fluoroquinolone
- Supportive care
- Limit the number of paroxysms
- Observe the severity of cough and provide assistance when necessary; Elevate head
- Maximize nutrition, rest, and recovery
- Azithromycin is the treatment of choice for all patients.
- Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole if a hypersensitivity to macrolides
- Prophylaxis for exposed/susceptible persons is also azithromycin for 5 days

Treatment of Pertussis
- paramyxovirus
- annual outbreaks, winter, mid-October - January
- A leading cause of hospitalization in US children
- Can also cause upper and lower respiratory tract infection in adults
- increasingly recognized severity in those with comorbid conditions
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)
Use these for diagnosis of what?
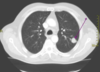
- Radiographically presents with nodular, irregular, pleural thickening, poss pleural effusion, and pleural plaquing
- CXR
- CT
- Thoracentesis
- Surgical biopsy
- Usually necessary for diagnosis
- Difficult to diagnose
- PET
- Helpful in ?malignancy; staging; poss surgical candidate
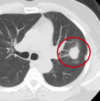
Mesothelioma
•2-5mm radio-opaque nodules on CXR
Dust particles in the alveoli are ingested by macrophages which then become “coal macules”
- HIV testing
- Interferon-gamma release assay (IGRA)
- Acid-fast bacilli (AFB) smear and culture with drug susceptibility
Using sputum from the patient collected in the early morning on how many consecutive days?
Diagnostic Tests for TB
3 consecutive days

- Complications include
- Respiratory failure for a minority of patients
- Malignancy
- Bronchogenic adenocarcinoma
- Malignant Mesothelioma (cancer arising from the mesothelial surface of the pleural cavity)
- Concomitant tobacco use increases risk of malignancy even more
- Treatment is supportive and preventative
Pneumoconiosis – Asbestosis
PCR assay is faster and more sensitive, but Nasopharyngeal swab is criterion standard for diagnosis
CBC will show leukocytosis with absolute lymphocytosis
Positive tests must be reported to state and local public health authorities
Diagnosis of Pertussis
•Alveolar ventilation (⩒A) ultimately determines the
PaCO2
- Recurrent, alveolar hemorrhage
- Children or young adults
- Iron deficiency
- Celiac disease.
- Treatment of acute episodes of hemorrhage with corticosteroids. Recurrent episodes of pulmonary hemorrhage may result in interstitial fibrosis and pulmonary failure.
Alveolar Hemorrhage Syndrome: Idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis:
Renal involvement and anti-glomerular basement membrane antibodies are absent, in contrast to Goodpasture Syndrome
- Symptoms last 5-7 days
- Edema and obstruction of these upper airways.
- Viral infection of the larynx, trachea, and the upper bronchial tree
- Most common between 7 and 36 months of age
- Lungs are typically clear to auscultation
Acute Laryngotracheitis / Croup

- Slowly progressive constitutional symptoms
- Malaise
- Anorexia
- Weight loss
- Fever
- Night sweats
- Chronic cough, productive with blood streaked sputum
Presentation of TB
- Patients typically present decades after relevant exposure with:
- Wait for it…
- Slowly progressive dyspnea, dry cough, and inspiratory crackles on exam…
Restrictive Lung Diseases Interstitial Lung Disease/Diffuse Parenchymal Lung Disease
Occupational Lung Diseases
Pneumoconiosis – Asbestosis
Pediatric Pneumonia, drug of choice for each age group?
- <4 weeks:
- 4-12 weeks:
- 3mo-5 yrs:
- >5yrs:
- <4 weeks: ampicillin and gentamicin or cefotaxime
- 4-12 weeks: IV ampicillin
- 3mo-5yrs: oral amoxicillin (if outpatient)
- >5 yrs: oral amoxicillin +/- a macrolide if an atypical organism is likely
Virchow triad?
(1) venous stasis
(2) activation of blood coagulation
(3) vein damage

- 2-5mm radio-opaque nodules on CXR
- Nodular opacities occur primarily in the upper lung fields in simple version
- May become more widespread and then confluent with progression to large opacities in complicated version with progressive massive fibrosis
Pneumoconiosis – Coal Worker’s Lung
simple coal workers pneumoconiosis
complicated coal workers pneumoconiosis
Which Alveolar Hemorrhage Syndrome?
- Idiopathic, recurrent alveolar hemorrhage
- Glomerulonephritis - rapidly progressive
- Occurs in men 30-40 yo
- Hemoptysis usual presenting symptom
- Dyspnea, cough, hypoxemia, diffuse bilateral alveolar infiltrates
- Iron deficiency anemia and microscopic hematuria (glomerulonephritis)
Goodpasture syndrome
- Abrupt onset (w/in 4-6 hrs) of fever, chills, malaise, nausea, cough, chest tightness, dyspnea.
- Exam: basilar crackles and tachypnea.
- CXR frequently normal
- Potentially confused with a viral or bacterial infection and given antibiotics
- Treatment: remove from environment
- Symptoms subside within 12hrs to several days.
Disease may recur with reexposure
ACUTE Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
- Transmitted via respiratory droplets
- Attacks ciliated epithelium
- Produces toxins —> inflammation and necrosis —> airway plugs, bronchopneumonia, and hypoxemia.
Pertussis
- Nasopharyngeal swab for culture is the Criterion standard for diagnosis but Takes a long time to get results and Must be cultured during catarrhal or paroxysmal phases
- PCR assays and antigen detection has Rapid results and More sensitivity and Can use later in the disease course
- CBC will show leukocytosis with absolute lymphocytosis
- Positive tests must be reported to state and local public health authorities
Diagnosis of Pertussis
- Since cause is most often viral, antibiotics not necessary.
- Avoid cough suppressants (try not to mess with the mucociliary clearance!)
- Okay to use at night if patient needs sleep
Treatment of Acute Bronchitis
Adult CAP Treatment
•Always cover _______?
Generally cover________?
- Outpatient:
- Inpatient:
- ICU:
S. pneumoniae
Atypicals
macrolide +/- B-lactam OR doxycycline
B-lactam + macrolide OR a respiratory fluoroquinolone
B-lactam + macrolide OR B-lactam + fluoroquinolone
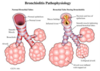
- Most cases caused by RSV
- Edema and cellular debris cause obstruction of small airways.
- most often in infants and young children.
- Most commonly in first 2 years of life.
- Peak age is 6 months.
- Leading cause of infant hospitalization.
Acute Bronchiolitis