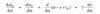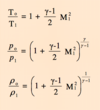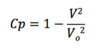GENERAL Flashcards
(179 cards)
Out of a metal alloy and a carbon fiber reinforced polymer (composite), which material is isotropic ?
The metal alloy is isotropic as the composite has preferred orientations for forces to be acted upon, this is related to the directions of the fibres, and thus the composite is not isotropic
Young’s modulus
represents the materials resistance to deformation
what are …
yield strength
failure strength
?
the stress at which plastic deformation starts
stress at which material fails
Max strain - on material properties table
max strain at which the material breaks
Specific property
gives the value of the property per unit density of the material
Thermoplastic
and
Thermoset polymers
Thermoplastic: It is one component and softening is reversible
Thermoset: It is made up off multiple components, and curing is irreversible
Polymer characteristics
isotropic
Low strength & stiffness
Huge variety
Plastic flow & melting
Good processibility
Low cost
Composites
Composed of more than one material
Fibre reinforced Polymers
Hybrid materials: GLARE
Anisotropic
when can they be usefull ??
having a physical property which is a different value when measured from different positions
strong and stiff in only one direction
Usefull when composite is tailored fibres, fibres coincide with loads.
Which material is stronger and which one strains more ?
Show this quantitatively.

To compare both rods you need to use
stress = σ = F/A
strian = ε = ∆L/L

Isotropic
the properties are independent of the direction the material is tested
Metal properties
Isotropic
can be strengthened
plastic behaviour ( can melt)
good processibility
often low cost
Week 3 Q.

thermoplastics can be heated and reshaped
Since composites consists of polymer and (one directional) fibres, composites are anisotropic (almost by definition)
Week 3 Q.

Because of their relatively thick structure, sandwich structures are difficult to bend (a bending moment is carried by facesheets at “large” distance from each other). Laminates need to be reinforced in order to carry bending loads. So this means only statement 2 is correct.
Though it is true that there is an expensive factor in the use of composites, that factor is not their processability, but the small volume of composites at this moment.

For fail safe multiple load paths should be created for each force:
(At least) TWO diagonal wires between A-C and also (at least) TWO wires between B-D
OR
(At least) One rod between A-C and also (at least) one rod between B-D

FOR SAFE Life one load path is assumed sufficient (but this path should have very low probability of failure during entire operational life)
TWO diagonal wires between A-C and also TWO wires between B-D
OR
One rod between A-C
OR
One rod between B-D
What can be seen on the primary flight display ?
Attitude, heading, airspeed and vertical airspeed
What does CDU stand for ?
What does it do ?
control and display unit
allows you to select a route or change a route
Identify the names of all compenents in this Glare cockpit


What is this called ?

Head-up display (HUD)
Primarily found in fighter jets.
KNOTS to M/S converion factor
0.5144…
ft/min to m/s conversion factor
0.00508
Why is the EAS used in the cockpit ?
the EAS is the measure for total dynamic pressure
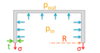
At an altitude of 24,000 feet a Pitot tube measures a total pressure of 0.5564 bar. Determine the equivalent airspeed (in metres per second) of the aircraft (assuming ISA conditions).