GI Flashcards
(91 cards)
VACTERL
Vertebral
Anorectal
Cardiac
Tracheal
Esophageal
Renal
Limb Anomalies
Esophageal atresia commonly occurs with what other anomaly?
Tracheoesophageal fistula
-distal esophagus connects with posterior trachea-
What is this? When does it present?
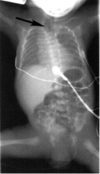
Esophageal atresia - maternal poly hydramnios
Vomiting up first feed
Reflux, back arching, stiffness, and torticollis
Sandifer’s Syndrome = GERD
What percentage of kids with GERD resolve without treatment by age 2?
60%
What is the most common cause of esophagitis?
Candida
How do you treat GERD?
Positioning after feeds
Thicken formula w/ rice cereal
Antacids, H2 blockers, PPIs
Motility agents = metoclopramide, erythromycin
How do primary gastric ulcers present in the first month of life, neonatal period, preschool, and > 6 yrs?
1st month: GI bleed/perforation
Neonatal: recurrent vomiting, slow growth
Preschool: Periumbilical, postprandial pain + vomiting
> 6 yo: epigastric abdominal pain, + blood loss/anemia
Gastric ulcers following surgery or head trauma?
Cushing
Stress gastric ulcers or those related with burns?
Curling ulcers
Colic
Frequent, complex abdominal pain and crying in infants < 3 months
Sudden onset loud crying
Circumoral pallor
Distended tense abdomen
Feet cold
*Relief with passage of feces/flatus*
Colic
R/o other causes
When and how does pyloric stenosis present?
Nonbilious vomiting
After 3 weeks, up to 5 months
What is the “olive” felt on exam of a pt. with pyloric stenosis?
Duodenal bulb
How do you diagnose pyloric stenosis?
U/S - 90% Senstive
What is this?

Pyloric stenosis
Also look for
string sign, double tract sign, shoulder sign
How does duodenal atresia present?
Bilious vomiting without abdominal distention
**First day of life**
What is this? How do you treat it?

Duodenal atresia - double bubble sign
NG tube, IVF, surgery
**Associated with malrotation, esophageal atresia, and heart disease**
Moms with polyhydramnios might have an infant with what?
GI atresia
How does volvulus present?
Gastric: Severe abrupt epigastric pain, intractible emisis - failure to pass NG tube
Intestinal: Vomiting, abdominal pain
What is the most common cause of acute intestinal obstruction under 2 yo?
Intussusception - Ileocolic (90%)
What things can cause “lead point” for intussusception to develop? (6)
Viral illness
Meckel’s diverticulum
Polyp
Lymphoma
Henoch-Schonlein purpura
CF
Intermittent colicky abdominal pain, bilious vomiting, and currant jelly stool.
Classic triad of Intussusception
Who do you diagnose intussusception?
US: Target/donut sign, Pseudokidney



