GI pathology Flashcards
(110 cards)
disease

dry socket
pseudomembrane candidiasis

acute atrophic candidiasis
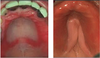
denture stomatitis

Both benign and no Tx
upper=> toris mandibularis
lower=> toris palatinus

erythema migrans (geographic tongue)

apthous ulcer
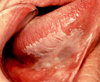
leukoplakia

odtongenic keratocyst

odontogenic keratocyst
lacks rete ridges
epithelial surface parakeratinized and often corrugated
basal cells hyperchromatic (cuboidal to columnar in shape w/ palisade nuclei)

amelioblastoma

Bisphosphonate related necrosis of jaw (BRONJ)

verrucous carcinoma

squamous cell carinoma

Left: Hiatal hernia => GEJ and Z line above diaphragm
Right: Barrett’s esophagus => Z line above GEJ

esophageal adenocarcinoma
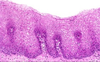
normal esophagus
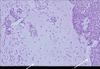
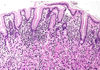
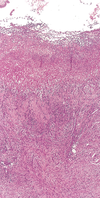
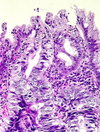
Describe this pathology

GERD
acid-pepsin injury increases cell death and desquamation at surface, w/ compensatory basal hyperplasia (+ elongated submucosal rete pegs)
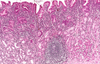
what is shown by the arrows in this pathology?

GERD
mucosal and submucosal lymphocytes, neutrophils, eosinophils
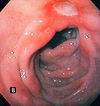
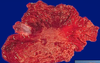
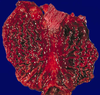
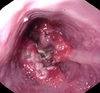
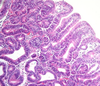
disease and what characterizes it grossly

Barrett’s esophagus
intestinal metaplasia
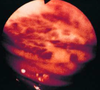
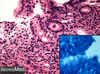
disease and what do arrows point to?

Barrett’s esophagus
goblet cells in columnar epithelium
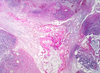
grade this disease
what does micro show?

low grade dysplasia of Barrett esophagus
crowded hyperchromatic nuclei
decreased goblet cell formation
grade this disease
what is found in micro

low grade dysplasia of Barrett’s esophagus
loss of cell polarity, but nuclei still mostly basal
some gland architectural irregularity => mostly not branched or back-to-back
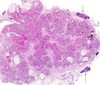
grade this disease
what is found in micro

high grade dysplasia or carcinoma in situ of esophagus
glandular architectural irregularity, nuclear atypia