GI Tract Flashcards
(59 cards)
Role of cholecystokinin
Gallbladder contraction Relaxation of sphincter of oddi
Pathway of bile from liver to duodenum
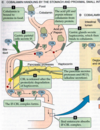
Liver to right and left hepatic ducts to common bile duct
cystic duct into gall bladder then to common bile duct joined by pancreatic duct and into duodenum via ampulla and sphincter of oddi

How bile is concentrated in gall bladder
Cl and sodium are pumped out in exchange of bicarbonate and water follows by osmosis
Intestinal lipid absorption
Before this, triacylglycerides are deesterified by lipase enzymes that separate the glycerol back bone from the hydrocarbon chains, forming glycerol and fatty acids (soluble).
- Long chain fatty acids converted back to triglycerides (reesterificatiom) in SER of intestinal endothelium, fat droplets form
- Apoproteins from RER go to SER and form chylomicrons and lipoproteins
- Chylomicrons migrate to membrane via vesicles, exocytose and go into lymphatic capillaries (lacteals)
- Short and medium chain fatty acids and glycerol go straight into cell and into bloodstream because water soluble

Function of bile
Allows for breakdown of fatty droplets, increasing surface area for lipases to react with. Bile salts also form vescicles around fats until they are absorbed
What lipases do
Breakdown TAG into glycerol group and fatty acids
Role of liver in bile formation
Conjugation of unconjugated bilirubin
Transport of bilirubin in plasma and liver
- Bilirubin from breakdown of erythrocytes travels in blood to liver bound to albumin
- In liver, it is conjugated and excreted into bile
- In ilium, bilirubin is converted to urobilinogen, then stirocobulin which is the excreted
- Part of the urobilinogen goes to the kidneys where it gives urine its yellow color.
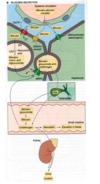
causes of Gallstones
Too much absorption of water from bile Too much absorption of bile Too much cholesterol in bile Inflammation of epithelium
Simulation of salivation. Parasympathetic and sympathetic, receptors and effects on secretion
Parasympathetic NS activate parotid and submandibular glands. Vasodilation. Causes profuse secretion of watery saliva with low organic material. Muscarinic receptors
Sympathetic stimulation of B adrenergic receptors via chorda lingual nerve. Vasoconstriction. Causes low amount of salivary secretion with high organic material

Functions of saliva
Digestive, protective, lubrication, speech
Salivary glands
Parotid gland
Submandibular gland
Sublingual gland
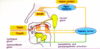
Primary secretion of saliva
In acinar cells concentration of ions isotonic to plasma Secretes proteins

Secondary secretion of saliva
in duct cells
Modified concentrations of ions
Na and cl reabsorbed, K and bicarbonate added
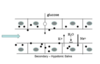
Effect of atropine
Lowers salivary secretion by blocking muscarinic receptors
Cephalon phase of acid secretion
Before and during food being eaten. Initiated via sight or smell, from brain to cells via parasympathetic vagus nerve
Gastric phase of acid secretion
How food stimulates it and what chemicals are involved
Phase of when food has been injested. Stimulates by stretching the stomach and raising stomach pH 3 chemicals stimulate HCl and intrinsic factor secretion: 1. Acetylcholine 2. Gastrin 3. Histamine
Intestinal phase of acid secretion
Initial stimulation of stomach by the arrival of chyme causing stretch of duodenum. Soon after, enterogastric reflex starts causing inhibition of parasympathetic stimulation and regulation via enteric nervous system CCK released
Retropropulsion
Bonus sent back to proximal stomach by contraction of pyloric sphincter
Intrinsic factor
Glycoproteins produced by parietal cells that combines with B12 to aid absorption in the ileum
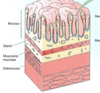
Stomach layers
Mucosa
Muscularis mucosa
Submucosa: connective tissue containing vessels
Muscularis: 3 layers of muscle
Serosa: outermost thin connective tissue
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
Cindition where rumors form in pancreas of duodenum that produce large amounts of Gastrin that through the circulation cause increased stomach acid secretion
How mucus and bicarbonate secretion create mucosal barrier
Bicarbonate is released by surface mucous cells and acts as a buffer by binding to H
Mechanism of secretion of HCl (endocrine and neurocine activation)
G cells, detect food and produce Gastrin in the bloodstream or ACh sends signal via muscarinic receptor.
Gastrin binds to CCK-2 receptors on ECL cells causing them to produce and release histamine.
Histamine binds to H2 receptors on parietal cells and
Parietal cells produce HCl