GI Tumours (upper tract) Flashcards
(45 cards)
What are the main types of benign oesophgeal tumour?
- Mesenchymal tumours
- Squamous papillomas
- Leiomyomas
- Fibromas
- Lipomas
- Haemangiomas
- Neuorfibromas
- Lymphangiomas
- Mucosal polys
- Squamous papillomas
What are the main types of malignant oesophgeal tumours?
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Adenocarcinoma
What are the rare types of maligant oesophgeal tumours?
- Carcinoid tumour
- Malignant melanoma
- Lymphoma
- Sarcoma
What are the main types of benign tumour of the stomach?
- Polyps
- Non-neoplastic
- Adenomas
What are the main types of malignant tumours of the stomach?
- Carcinoma
- Lymphoma
- Carcinoid
- Mesenchymal
What is the incidence of squamous cell carcinoma of the oeosphagus?
- > age 50
- 5 per 100,000 population in males and 1 per 100,000 in females (average in Europe)
- Male = 2:1
- Female = 20:1
- Geographical variation
- Iran, Central China, South Africa and Southern Brazil
What are the main factors assoicated with SSC of the oesophagus?
- Dietary
- Deficiency of vitamins (A, C, thiamine, pyridoxine)
- Fungal contamination of food stuffs
- High content of nitrites/nitrosamines
- Lifestyle
- Burning-hot beverages or food
- Alcohol and tobacco
- Oesophageal Disorders
- Long-standing oesophagitis and achalasia
- Genetic predisposition
What is the likelihood of SSC occuting in each third of the oesophagus?
- 20% in the upper third
- 50% in the middle third
- 30% in the lower third of oesophagus
What is the gross morphology of SCC of the oesophagus?
Small, grey-white, plaque-like thickenings that become tumorous masses
What are the 3 main patterns of morphology of SCC of the oesophagus?
- Protruded polypoid exophytic (60%)
- Flat, diffuse, infiltrative
- Excavated, ulcerated
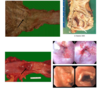
Describe the histology of SCC
- The squamous epithelium
- Pleiomorphism
- Hyperchromatism
- Miotic figures
- The degree of atypia:
- Low grade dysplasia
- High grade dysplasia
Describe the clinical features of SCC of the oesophagus
- Dysphagia
- Extreme weight loss (cachexia)
- Haemorrhage and sepsis
- Cancerous tracheoesophageal fistula
- Metastases (lymph nodes):
- Cervical
- Mediastinal
- Paratracheal
- Tracheobronchial
- Gastric and celiac
What is the prognosis of oesophageal SCC?
5% overall five-year survival
What part of the oesophagus does adenocarcinoma affect?
The lower third of the oesophagus
originates from the glandular tissue
What does adenocarcinoma of the oesophagus arise from?
- Arise from Barrett Mucosa (10%)
- Intestinal metaplasia caused by gastric reflux
What is the average age of onset of oesophgeal adenocarcinoma?
Age 40, with a median age of 60
What are two main causative factors assoicated with adenocarcinoma?
tobacco and obesity
Describe the morphology of oesophgeal adenocarcinoma
- Flat or raised patched or nodular masses
- May be infiltrative or deeply ulcerative
- Histology:
- Mucin-producing glandular tumours
Describe the T of TNM staging
T is carcinoma in situ
T1 = invasion of submucosa
T2 = invasion of muscularis propria
T3 = invasion of adventitia
T4 = invasion of adjacent structures
Describe the N of TNM staging
N0 = no node spread
N1 = regional node metastases
Describe the M of TNM staging
M0 = No distant metastases
M1 = Distant metastases
What are the main clinical features of oesophgeal adenocarcinoma?
- Dysphagia
- Progressive weight loss
- Bleeding
- Chest pain
- Vomiting
- Heartburn
- Regurgitation
- Prognosis: 20% overall five-year survival
What is a polyp?
Nodule or mass that projects above the level of the surrounding mucosa, usually in the antrum
Describe non-neoplastic polyps
- Most are small and sessile (without a stalk)
- Hyperplastic surface epithelium
- Cystically dilated glandular tissue
90% of polyps











