Haemorrhagic Stroke Flashcards
(17 cards)
What is a haemorrhagic stroke and what is the main differentiating feature from a ischaemic stroke (that a patient would tell you)?
A stroke that occurs because a vessel in the brain has burst leading to symptoms
This CAUSES PAIN, Unlike ischaemic
What are the risk factors for haemorrhagic stroke?
Hypertension
Anti coagulation therapy or thrombolysis
Trauma
What would a haemorrhagic stroke look like on a CT?
Blood is white so it would appear white on CT
Most haemorrhagic strokes from the arteries appear around the centre of the brain from an anuerysm. eg berry top aneuysm on Basilar Artery

What is primary intercerebral haemorrhage?
This occus when a vessel ruptures and causes the symptoms of a stroke. (symptoms depends where it is).
This typically occurs on the someone with anticoagulant therapy.

What is a subarachnoid haemorrhage and what are the symptoms and what normally causes it?
This is a bleed under the arachnoid mater.
- Characteristic THUNDERCLAP HEADACHE
- Meningism - photophobia
- Caused by aneurysm or infection

What is a central venous thrombosis and what are its characteristcs and what shouldnt it be treated with?
This is a block in the venous drainage of the brain which leads to a burst and symptoms
- It is subacute, evoving over time
- It has no respect for arterial territories
- It usually affects the young
- it causes raised ICP
- Althought it is a bleed, treat with anti-coagulants as this caused the issue in the first place

What does a CVST(central venous thrombosis) look like on a CT - Where is it likely to be found and what does it follow?
They are more lilkely to haemorrhage around the peripheries of the brain and don’t follow arterial boundaries

What colour is blood on a CT?
White
What are the risk factors for CVST?
DVTs
Dehydration
Thrombophilia
Pregnancy
What are the symptoms of an intercerebral haemorrhage?
Headache
Nausea and vomiting due to raised ICP
Papilloedema
Cushings Reflex
Hemiparesis/hemiplagia
What type of stroke is associated with a berry aneurysm?
Subarachnoid
What is this?

Left sided acute on chronic subdural haematoma
What is this?
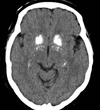
bilateral basal ganglia calicification
What is this?

right sided acute SAH
What is this?

WHITE MEANS ACUTE
right acute intra cerebral haemorrhage
What is this?
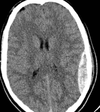
WHITE MEANS ACUTE
Left Acute extra dural haematoma
What is this?
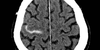
right acute SAH


