HD2 Qs Flashcards
mBob, 70-years-old, presents to his General Practitioner (GP) complaining of frequent urination accompanied by a burning sensation and interrupted flow of urine that have been going on for about 4 months. Digital rectal examination reveals an enlarged, nodular prostate and his prostate- specific antigen (PSA) levels are very high. After his biopsy results come back, he is diagnosed with prostate cancer. Which prostatic zone typically enlarges with prostatic cancer?
Transitional zone
Periurethral gland region
Fibromuscular zone
Central zone
Peripheral zone
Bob, 70-years-old, presents to his General Practitioner (GP) complaining of frequent urination accompanied by a burning sensation and interrupted flow of urine that have been going on for about 4 months. Digital rectal examination reveals an enlarged, nodular prostate and his prostate- specific antigen (PSA) levels are very high. After his biopsy results come back, he is diagnosed with prostate cancer. Which prostatic zone typically enlarges with prostatic cancer?
Transitional zone
Periurethral gland region
Fibromuscular zone
Central zone
Peripheral zone
A 72-year-old man presents with symptoms and signs of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Which one of the following structures is most likely to be enlarged?
Posterior lobe of the prostate
Median lobe of the prostate
Right lateral lobe of the prostate
Left lateral lobe of the prostate
Anterior lobe of the prostate
A 72-year-old man presents with symptoms and signs of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Which one of the following structures is most likely to be enlarged?
Posterior lobe of the prostate
Median lobe of the prostate
Right lateral lobe of the prostate
Left lateral lobe of the prostate
Anterior lobe of the prostate
A 26-year-old man attends the GP with abdominal pain and diarrhoea. The GP suspects gastritis but checks his urine in case of a UTI. The results are as follows:
Blood Neg mmol/l
Protein Neg mmol/l
Leukocytes ++ mmol/l
Nitrites Neg mmol/l
Which of the following is an explanation for the abnormal urine dipstick result?
Benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH)
Chlamydia
Ureteral stricture
Neurogenic bladder
Diarrhoea
A 26-year-old man attends the GP with abdominal pain and diarrhoea. The GP suspects gastritis but checks his urine in case of a UTI. The results are as follows:
Blood Neg mmol/l
Protein Neg mmol/l
Leukocytes ++ mmol/l
Nitrites Neg mmol/l
Which of the following is an explanation for the abnormal urine dipstick result?
Benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH)
Chlamydia
Ureteral stricture
Neurogenic bladder
Diarrhoea
An 84-year-old man admitted to the neurology ward informs the nurse that he is unable to urinate. He appears significantly distressed and reports pain due to urinary retention. The nurse places him in a warm bath, where the patient is finally able to relax his sphincter and urinates.
Which of the following nervous structures was responsible for maintaining detrusor capacity and making it difficult for the patient to urinate?
Hypogastric plexuses
Inferior mesenteric plexus
Pelvic splanchnic nerves
Prostatic hyperplasia
Pudendal nerve
An 84-year-old man admitted to the neurology ward informs the nurse that he is unable to urinate. He appears significantly distressed and reports pain due to urinary retention. The nurse places him in a warm bath, where the patient is finally able to relax his sphincter and urinates.
Which of the following nervous structures was responsible for maintaining detrusor capacity and making it difficult for the patient to urinate?
Hypogastric plexuses
Inferior mesenteric plexus
Pelvic splanchnic nerves
Prostatic hyperplasia
Pudendal nerve
A neonate born with clubbed feet dies shortly after birth due to severe respiratory distress. His mother had not sought antenatal care. Post-mortem shows pulmonary hypoplasia.
Which of the following clinical features would most likely also be present?
Bilateral renal agenesis and oligohydramnios
Bilateral renal agenesis and polyhydramnios
Cleft palate
Oesophageal atresia and oligohydramnios
Oesophageal atresia and polyhydramnios
A neonate born with clubbed feet dies shortly after birth due to severe respiratory distress. His mother had not sought antenatal care. Post-mortem shows pulmonary hypoplasia.
Which of the following clinical features would most likely also be present?
Bilateral renal agenesis and oligohydramnios
Bilateral renal agenesis and polyhydramnios
Cleft palate
Oesophageal atresia and oligohydramnios
Oesophageal atresia and polyhydramnios
Which structure does the uterine artery pass over?
Round ligament
Ovarian ligament
Ureter
Ovary
Which structure does the uterine artery pass over?
Round ligament
Ovarian ligament
Ureter
Ovary
Complete the sentence: The ovarian ligament connects the ovary to the ______________.
Lateral surface of the uterus
Labia majora
Lateral abdominal wall
Pubic symphysis
Complete the sentence: The ovarian ligament connects the ovary to the ______________.
Lateral surface of the uterus
Labia majora
Lateral abdominal wall
Pubic symphysis
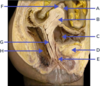
Label A-E of female anatomy [5]

A: bulb of the vestibule
B: levator ani
C: Obturator internus muscle
D: Left ureteric orifice
E: Muscular coat of urinary bladder

Label A-E

A: vagina
B: crus of clitoris
C: labia minoria
D: glands of clitoris
E: cervix

Label A

Vesico-uterine pouch
Label A-E

A: round ligament
B: broad ligament
C: suspensory ligament
D: uterine ligament
E: ovarian ligament
Label: 2, 3, 7, 8 and 10 [5]

2: uterine ligament
3: ovarian ligament
7: ureter
8: rectum
10: bladder
Which is the recto-uterine pouch? [1]

14

Label A-E

A: Clitoris
B: Labium minorum
C: bulb of vesitubule
D: ischiocavernous
E: Bartholin gland / greater vestibular gland

Label A-D

A: Perineal branches of pudendal nerve
B: Levator ani muscle
C: Inferior rectal nerves
D: Gluteus maximus muscle

Label the nerves of External female genital organs highlighted [4]

5:Dorsal nerve of clitoris
8 Perineal branches of pudendal nerve:
15: Pudendal nerve and internal pudendal artery
16: Inferior rectal nerves
Label A-F

A: ureter
B: uterine artery
C: levator ani muscle
D: vagina
E: round ligament
F: uterus
Which immunoglobins are produced when have antisperm antibodies? [3]
Develop antisperm antibodies (ASA): IgG, IgA and IgM
Which artery is 14? [1]

Internal iliac artery
label 1-9

1 Glans of clitoris
2 Labium majus
3 Vestibule of vagina
4 Hymen
5 Posterior labial commissure
6 Body of clitoris
7 Labium minus
8 External orifice of urethra
9 Vaginal orifice

Label 1-3 & 6-9

1 Body of clitoris
2 Crus of clitoris
3 Bulb of vestibule
4 Prepuce of clitoris
5 Glans of clitoris
6 Frenulum of clitoris
7 Labium minus
8 Vaginal orifice
9 Greater vestibular gland
Label the highlighted numbers [4]

11 Ilio-inguinal nerve
13 Superficial inguinal ring
14 Round ligament of uterus
16 Aponeurosis of external abdominal
oblique muscle
Label the highlighted guys [3]
24 Levator ani muscle
25 Pudendal nerve and
internal pudendal artery
26 Inferior rectal nerves

Label 1-14

1 Ilium
2 Rectum
3 Recto-uterine fold
4 Ovary
5 Uterine tube
6 Urinary bladder
7 Urethra
8 Labium minus
9 Recto-uterine pouch of
Douglas
10 Uterus (uterovesical
pouch)
11 Ligament of the head of
the femur
12 Head of femur
13 Vestibule of vagina
14 Labium majus