Helminthology Flashcards
(62 cards)

Moniezia expnasa

Diphyllobothrium latum - Broad or fish tapeworm
- One set of genitalia
- genital openings are on the middle line of proglottids

Dipylidium caninum - flea or cucumber tapeworm
- anapolytic: can move in feces and push eggs out

Moniezia expansa
- triangular shape
- 6 hooked oncoshophere is central

Lancet fluke egg
- detected by flotation
- with two eye-like excretory cells of the miracidium inside.
- the egg is hard-shelled

Liver fluke: big lesions
Lancet fluke: smaller lesions

2nd larval form: sporocyst, produces redia
- develops in the body of the snail

Moniezia benedeni
- quadrangular eggs
- 6 hooked oncoshaera is eccentric

Liver: big lesions: T. tenuicollis.
Small lesions: pisiformis / echinococcus

Strobilocercus fasciolaris
- with seperated bladders
- in liver of rodents
only taenia that can infect cats

Egg of rumen fluke
- unembryonated egg. collected from fresh feces
- the eccentric zygote is surrounded by coarse yolk granules

primary biotope for intermediate host snail of liver fluke

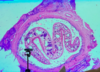
Liver fluke adult, hemorrhages

Cysticercus longicollus
- short neck
- predilection site: body cavity of rodents

Lancet fluke adult
- food source: absorbs nutrients from bile
- two larger testicles and the smaller ovary are behind the ventral sucker while yolk glands are lined up on both sides of the worm

Egg of liver fluke
- non-embryonated egg. observed in fresh feces.
- the eccentric zygote is surronded by a finely granulated yolk
Liver fluke with blood inside

Blood fluke, egg

Cercaria of Fasciola hepatica
- develops inside the body of a redia
- after rain the cercaria swarm out of the snail and swim to find a solid surface.
- cercariae attaches to vegetation, shed their tail and encyst as metacercariae (the infective stage)

Egg of anoplocephala

Anoplocephala

Cercaria of blood fluke

Schematic drawing of T.multiceps

Galba truncatula with metacercariae around