Hemorhagicc stroke Flashcards
(15 cards)
What are the risk factors for Intraparenchymal hemorrhage?
Hypertension Coagulopathy Vascular malformation (Aneurysm, AVM) Tumor (EG. Melanoma, Cerebral amyloid angiopathy)
Where is the usual locations of a hypertensive hemorrhage?
- Deep Gray Nuclei (Basal Ganglia, Thalamus)
- Pons
- Cerebellum
Pic: example of basal ganglia and talmus hemorhage

Example of pons and cerebellum image

What is a hemorhage at the grey white junction of the cerebrum suggestive of?
a underlying metastatic lesion

Cerebral amyloid angiopathy
ussually found in older patients

How do you manage a intraparachymal hemorhage?
- Blood pressure control
- Address coagulopathy
- Identify/address underlying structural abnormality
- Consider Neurosurgical decompression
Interventricular hemorhage
hydrocephaly could be a problem
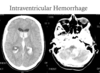
Subdural hematomal
low pressure-venous blood
blood is irritating to the brain
old people are ussally the problem because thier brain shrinks, recurents can happen

What is diagnostic of Epidural Hematoma?
- High pressure arterial bloodflow
- Middle Meningeal Artery
- Lucid Interval
lens shaped

What are risk factors of venous sinuses thrombosis?
Hypercoagulable
- Genetic
- Pregnancy
- Malignancy
- Inflammatory disease
- Infection
Pic: left side is venous rupture. bloody because blood cant leav via veins
Right: pale with cherry macula

What is a thunderlap headche?
aneurysmal subarachnoid
Traumatic sub rachnoid

Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorhage?
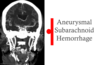
Traumatic subarachnoid hemorhage

How are subarachnoid hemorhage diagnosed?
- Noncontrast CT
- If CT nondiagnostic–Lumbar puncture (Elevated RBCs in CSF, Elevated RBCs in tubes 1-4-if blood is in all tubes, Xanthochromia-pigment released from RBCs in the CSF, Consider repeating 6 hours after onset of symptoms)
- Angiography
What are complications of Subarachnoid hemorhage?
- Death- a lot die)
- Re-bleed (Early clip or coil)
- Seizure
- Hydrocephalus
- Vasospasm(Peak day 8)- irritation by blood, can have ishema stroke
- Nimodipine
- Pulmonary edema
- Cardiac arrhythmia
- Hyponatremia


