High Yield: Surgery Flashcards
(54 cards)
With abdomen trauma, if they’re hemodynamically stable, what to do? Stab wound?
CT abdomen
What’s the next step if stab wound, unstable and have peritonitis?
Exploratory laparotomy
Describe: Tamponade
Beck’s triad
- low blood pressure (weak pulse or narrow pulse pressure)
- muffled heart sounds
- raised jugular venous pressu
What’s the difference between tamponade and tension pneumothorax? (2)
- cardio tamponade: no respiratory distress
- tension pneumothorax: respiratory distress and trachyal deviation
What’s the dx of cardiac tamponade? (3)
- Clinical
- If insure: FAST echo
- If dx clear: pericardiocentesis
What’s the dx of tension pneumothorax? What’s the management? (2)
- Clinical dx
- Management: Needle thoracentesis to alievate air escape, followed by chest tube.
- key: trachial deviation
- if normal pneumothorax, just chest tube
If trauma to the head with an unconscious period, what to do? (1)
Head CT without contrast
If CT head negative and orienté x 3, what to do?
They can go home
Identify. What’s the tx?

- Epidural hematoma (lens shape)
- tx: emergency craniotomy
Describe presentation: Epidural hematoma (lens shape) (3)

- lucid interval
- knocked out
- wake up a bit, then pass out again
What’s the tx: Increased cranial pressure (3)
- Elevating head
- Hyperventilating
- Mannitol (osmotic diuretic) which helps draw fluid into vasculature to alleviate edema
Describe tx: Hemothorax (2)
- Usually resolves on its own
- If > 1.5 L or > 200 ml/per hour for 4h -> intercostal artery injury, surgical procedure (video assisted thorascopic surgery VATS)
Name complications: Blunt trauma to chest (3)
- Pulmonary contusion
- Myocardial contusion
- Transection of the aorta
Identify

L Pulmonary Contusion 24h after blunt trauma
tx: supportively
Describe: Myocardial contusion (3)
- trauma to the sternum
- EKG, troponin
- associated with fx to sternum
Describe: Transection of the aorta (3)
- Associated with high falls and motor vehicle crash with sudden deceleration
- on x-ray: widened mediastinum
- associated with first rib fx, scapula and sternum

Name 1st-line imagery: Transection of the aorta (1)
CT angio

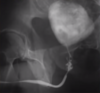
Bladder injuries diagnosed with what?
- Retrograde cystogram
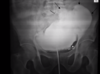
In retrograde cystogram, if leakage in into peritoneum, what to do? (2)
- = introperitoneal bladder injury
- tx with surgery and close with suprabucic ostomy tube

Describe tx: Extraperitioneal injury of the bladder (bellow peritoneum)
Foley catheter
Describe: Renal injury (2)
- Associated with lower rib fx (11th and 12th fx)
- Gross hematuria
Describe dx and tx: Renal injury (2)
- Dx: CT
- Tx: self-resolving
Describe: Urethral injury (3)
- Blood at meatus
- Possible scrotal hematoma, inability to void
- High-riding prostate

Describe dx: Urethral injury
-
dx: retrograde uretrogram
- no foley catether bc can make injury worse