Histo Flashcards
(112 cards)
1
Q

A
Kidney - Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
2
Q

A
Vagina

3
Q

A
Trachea

4
Q

A
Gallbladder

5
Q
A
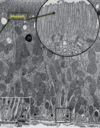
Microvilli

6
Q

A
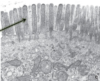
Cilia
7
Q

A
Liver
8
Q

A
Clathrin-Coated Pits
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
9
Q

A
Arrows point to Nuclear Pore Complex (NPC)
10
Q
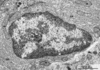
A
Chromatin in Nucleus

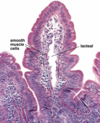
11
Q

A
H&E stain of smooth muscle
12
Q
A

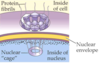
13
Q

A
Nuclear Pores
14
Q

A

15
Q
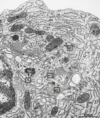
A
16
Q

A
cell movement
17
Q

A
Mitochondria in Heart Muscle
18
Q
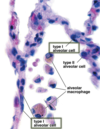
A

19
Q

A
Trachea
Scanning EM
20
Q
A

21
Q
A
Mitochondria in Liver
22
Q
A
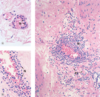
Neutrophil Migration:
a. white blood cells in blood vessel
b. after diapedesis
c. after chemotaxis
23
Q

A

24
Q
A
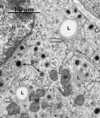
Lipid on EM
25

rER
26

Nucleus
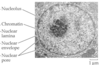
27

Male Reproductive Tract

28
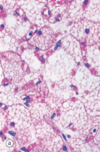
Lipid stained with H&E
29

Lysosome

30
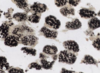
Lipid stained with Osmium Tetroxide (OT)
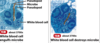
31

Phagocytosis
32
Urinary Bladder

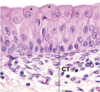
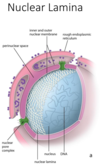
33

Lamin A mutation; Hutchinson Gilford Progeria (aging)
34
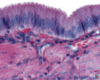

35
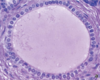

36

Glycocalyx

37
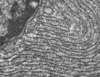
rER

38

Trachea
## Footnote
Transmission EM
39
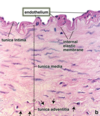

40
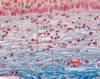

41

Actin
## Footnote
microvilli & stereocilia
fast growing + end, slow - end

42

Uterine Tube
43
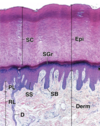
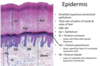
44

Pinocytosis
45
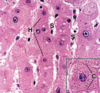
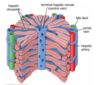
Liver Hepatocytes

46

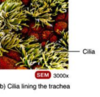
47
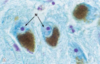
Melanin

48

Peroxisomes
## Footnote
Important role in fat metabolism
Very long chain fatty acid (VLCFA) beta-oxidation
Peroxisomal proteins are synthesized by free (cytoplasmic) ribosomes

49
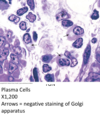
50
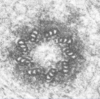

51


52

Small Intestine

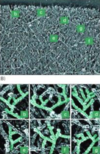
53
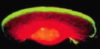
Red = Actin
Green = ARP Complex (Actin Related Proteins)
ARP complex highly concentrated near front of lamellipodia where actin nucleation most active
54
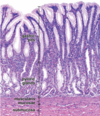

55

Ovary
## Footnote
Simple cuboidal epithelium
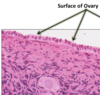
56
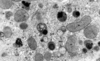
Lysosomes

57


58
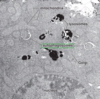
Autophagy
## Footnote
Autophagosome = double membrane vacuole
fuses with lysosome
Clinical correlation: Essential role in starvation, cellular differentiation, cell death and cell aging
59

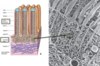
Microvilli
## Footnote
About 20- 30 actin filaments are found in the core of each microvillus
60

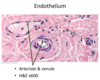
61

Stereocilia = really long microvilli
## Footnote
Epididymis, Proximal ductus deferens, Sensory hair cells of inner ear
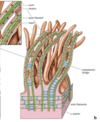
62

Golgi
63

Golgi

64

rER
65

Trachea

66

Mitochondria
Cilincal Correlation = Mitochondriopathies
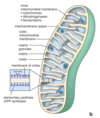
67

sER
68

Esophagus

69


70

Kidney Tubules

71

Intermediate Filaments
## Footnote
Rope-like, nonpolar
Stabilize cell structure, Resist shearing forces
Connecting with desmosomes & hemidesmosomes
72

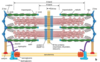
73

Cilia
74
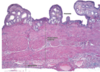

75


76
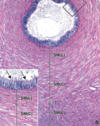
Male Reproductive Tract

77

Mallory stain of a peripheral nerve
78
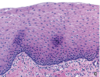

79

Glycocalyx
80

Stratified Columnar Epithelium

81
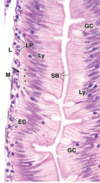
Small Intestine

82

sER
lipid metabolism: cells that synthesize and secrete steroids
detoxification (hepatocytes and detoxifying enzymes)
Cytochrome P450 System
Sequesters Ca2+ (muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum)

83
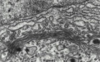
Golgi
84


85
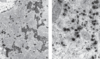
Glycogen
86


87

Azan stain of nerve ganglion
88


89
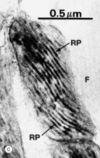
Mitochondria

90
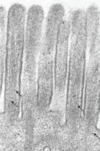
Microvilli
## Footnote
crosslinked by villin, anchored in terminal web
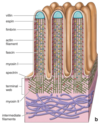
91

92
Microtubule-based, antennae-like structure (9 + 0)
Emanates from almost all cells
Anchored to cell via the basal body
Develops from one centriole following cell division

93
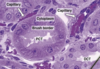
Microvilli

94
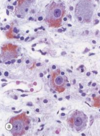
Lipofuscin
## Footnote
Sympathetic Ganglion Cells stained with H&E
95


96
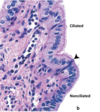
Uterine Tube
97
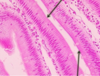
Microvilli Brush Border
## Footnote
Core composed of actin microfilaments
Anchored to a actin network structure called the terminal web
Increasing the apical surface area of the
cell
ABSORPTION
98
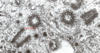
Centrioles
9 triplets of microtubules arranged around a central axis
## Footnote
Each triplet consists of 1 complete and 2 incomplete microtubules fused
Organize the centrosome
Basal body formation
Provide basal bodies necessary for assembly of cilia and flagella • Mitotic spindle formation
Formation of centrosome & alignment of the mitotic spindle during cell division

99

Stomach
## Footnote
Simple columnar epithelium
H&E x120
100

Cilia
## Footnote
Kartagener syndrome/Primary ciliary dyskinesia
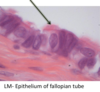
Location: Respiratory Epithelium, Fallopian Tube
101

Secondary Lysosomes
102
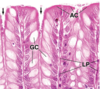
Large Intestine

103
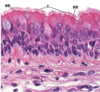

104

Phagocytosis
105
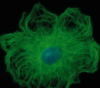
Microtubules

106

Thyroid Follicles

107

Receptor Function
## Footnote
Receive & transduce external stimuli
Ex. Olfactory epithelium of the nasal mucosa
H&E x240

108

Nucleolus: Ribosome Factory

109

110

Large Intestine

111

Movement produced by the bending of the core (axoneme)
dynein motors produce a bending movement

112




