Histology Flashcards
(86 cards)
1
Q

A
Simple Cuboidal
2
Q

A
Pseudostratified Columnar
3
Q

A
Simple Columnar
4
Q

A
Stratified Columnar
5
Q
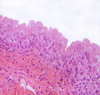
A
Transitional
6
Q

A
Stratified Cuboidal
7
Q

A
Simple Squamous
8
Q

A
Stratified Squamous
9
Q

A
Adipose
10
Q

A
Blood
11
Q

A
Osteous (bone)
12
Q

A
Hyaline Cartilage
13
Q

A
Areolar
14
Q

A
Dense Irregular
15
Q

A
Dense Regular
16
Q

A
Reticular
17
Q

A
Elastic Dense
18
Q

A
Fibrocartilage
19
Q

A
Elastic Cartilage
20
Q

A
Skeletal Muscle
21
Q

A
Cardiac Muscle
22
Q

A
Smooth Muscle
23
Q

A
Neuron/Neuroglia
24
Q
Tissues
A
Cells that work together to perform a function
25
Histology
Study of tissues
26
Extracellular Matrix
A network of proteins that provide the structural and biochemical support for surrounding cells
27
Functions of Epithelial Tissue
Physical protection, control permeability, provide sensation, produce specialized secretions
28
Location of Epithelial Tissue
cover body surface, cover and line internal organs, and compose glands
29
Epithelia
Layers of cells that cover internal or external sufaces, have gland cells
30
Exocrine glands
Secrete on external areas of the body
31
Endocrine glands
Secrete hormones into interstitial fluid
32
Distinguishing Characteristics of Epithelial Tissue
Tightly packed cells, lack of blood vessels, free surface, basement membrane, readily divide
33
Simple Squamous
* Single, thin, flat layer
* Absorption and diffusion
* Kidney passages, inside eye, alveoli of lungs
* Slippery surface reduces friction
34
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
* where mechanical/chemical stresses are severe
* series of layers
* skin, mouth, throat, esophagus, rectum, anus, vagina
* keratinized/non-keratinized
35
Keratinized
found on skin surface, abrasion resistant
36
Non-Keratinized
Resists abrasion but can dry out
37
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
* line exocrine glands and ducts
* portions of kidney
* secretory chambers of thyroid gland
38
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
* rare
* ducts of various exocrine glands (skin)
39
Transitional epithelium
* stretches and recoils
* bladder, urine-collecting chambers of kidneys
* relaxed, plump, and cuboidal
40
Simple columnar epithelium
Stomach, intestine, uterine tubes, kidney ducts
41
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
* relatively rare
* only superficial cells are columnar
* rare ducts of salivary glands and pancreas
42
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
* nasal cavities, trachea, larger airways of lungs
* cilia move substances
* appear stratified
* every cell attached to basal lamina
43
Connective tissue
most abundant and widely distributed tissue in the body, never exposed to outside, blood vessels and sensory receptors
44
Basic Components of Connective Tissue
* specialized cells
* extracellular protein fibers
* fluid (ground substance) - more than epithelial
45
Function of Connective Tissue
* structural framework for the body
* transport fluids and dissolved materials
* protect delicate organs
* support, surround, interconnect other types of tissue
* store energy reserves (triglycerides)
* defend from invading microorganisms
46
Distinguishing characteristics of connective tissue
* matrix between cells
* good blood supply
47
Extracellular protein fibers of connective tissue
* reticular - strong branching network
* collagen - thick, very strong
* elastic - slender, stretchy
48
Fluid of connectice tissue
clear and colorless, syrupy due to proteins
49
Melanocytes
synthesize melanin, fixed
50
fixed macrophages
engulf cell debris and pathogens, fixed
51
Mast cells
stimulate inflammation and mobilize defenses, fixed
52
fibroblasts
synthesize extracellular fibers, fixed
53
Adipocytes
store lipid reserves, fixed
54
plasma cells
immune cell producing antibodies, wandering
55
free macrophages
consume debris and pathogens, wandering
56
Mesenchymal cells
stem cells that aid tissue repair, wandering
57
neutrophils and eosinophils
phagocytic blood cells, wandering
58
lymphocytes
immune stem cells, wandering
59
Loose connective tissue proper
fibers create loose, open framework
60
areolar (loose connective)
* most common connective proper
* packing material of the body
* wraps/cusions organs
* has all connective tissue proper cell types
61
adipose (loose connective)
* deep to skin
* mostly cells (adipocytes)
62
Reticular (loose connective)
* liver, kidney, spleen, lymph nodes, bone marrow
* provides support and resists distortion
* many reticular fibers forming network
63
Dense Connective Tissue Proper
* fibers densely packed
* desnse regular
* dense irregular
* elastic
64
Dense Regular
* tendons and ligaments
* parallel collagen fibers
65
Dense Irregular
* visceral organs, superficial layers of bones, cartilages, and peripheral nerves, dermis
* no consistent pattern of fiber arrangement
66
Elastic
* more elastic fibers than collagen
* springy and resilient
* between vertebrae, walls of large blood vessels
67
Fluid Connective Tissue
Blood and lymph, fluid matrix with suspended proteins, normally without fibers
68
Blood
* plasma-watery matrix
* cells and cell fragments
* moved by heart through blood vessels
* exchanges water and solutes between plasma and interstitial fluid
69
lymph
* lymphatic vessels
* collected from interstitial fluid
* returned to blood at large veins near heart
* maintain solute levels, blood volume, and alert immune system of infection
70
Supporting connective tissue
cartilage and bone
71
Cartilage
* solid, rubbery matrix of firm gel
* chondrocytes are cells
* small chambers (lacunae)
* set apart by perichrondrium
72
hyaline cartilage
* between ribs and sternum, bones in mobile joints, areas of respiratory system
* most common
* stiff flexible support reduces friction
73
Elastic Cartilage
* External ear and other smaller internal structures
* increased flexibility
74
Fibrocartilage
* knee joint, pubic bones or pelvies, invertebrate discs
* resists compression, prevents bone to bone contact, limits relative movement
75
Bone
* solid, crystalline matrix
* small amount of ground substance
* 2/3 matrix is calcium salts
* mostly calcium phosphate and some calcium carbonate
* many collagen fibers
76
Muscle tissue
* 40% of body weight
* smallest muscle in inner ear
* over 600 muscles in the human body
* can only contract
77
Functions of muscular tissue
* movement of body
* movement of blood around cardiovascular system
* movement of materials around digestive tract
78
Locations and types of Muscular Tissue
* skeletal muscle attached to bone
* smooth muscle in walls of hollow organs
* cardiac muscle in heart
79
Skeletal Muscle
* long, cylindrical, striated, multinucleate cells
* voluntary
* moves skeleton, guards organ entrances for digestive, respiratory, urinary, generates hear, and protects internal organs
80
Cardiac Muscle
* short, branched, single nucleus cells
* connected by intercalated disks
* involuntary
* move blood, maintain blood pressure
81
Smooth Muscle
* involuntary
* short, spindle-shaped, single nucleus cells
* move food, urine, reproductive secretions, control diameter or respiratory passageways and blood vessels
82
Distinguishing Characteristics of Muscular Tissue
* thin, elongated, cylindrical cells
* elongated nuclei
* contractile
83
Nervous Tissue
* 98% in brain and spinal cord
* 2% in nerves
* conduction of electrical impulses
* axon, dendrites, neurological cells, neuron
84
Neurons
transfer information around body, process information
85
Neuroglia
Maintain physcial structure of neural tissue, provide nutrients to neurons
86
Distinguishing Characteristics of Nervous Tissue
cells have long tendrils, communicate to each other and other body parts


