Histology Flashcards
(154 cards)
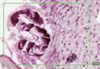
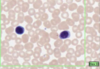
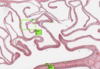
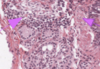
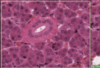
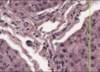
What is this slide stained with? What stains blue with this stain?

Alcian blue
- GAG rich structures
- Mucous
- Mast cells
- Cartilage
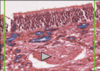
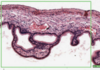
What is this slide stain with?
What stains pink with this stain?
Eosin
- Colloidal proteins
- Plasma
Eosinophilic = Acidophilic
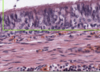
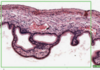
What is this slide stained with?
What stains black with this stain?

Iron haematoxylin
- Nuclei
- Elastic fibres
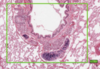
What is this slide stained with?
What stains magenta with this stain?
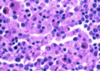
- Hexose sugars
- Goblet cell mucins
- Cartilage matrixs
- Glycogen
- Basement membranes
- Brush border
What is this slide stained with?
What stains:
- Purple
- Red/pink
- Pale blue
- Dark blue

Purple = chromatin/nuceli and netrophil granules
Red/pink = Erythrocytes/eosin granules
Pale blue = Lymphocyte/monocyte plasma
Dark blue/purple = Basophil granules
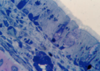
What is this stained with?
What stains:
Dark blue
Pale blue
Bright purple
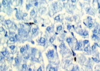
Toludine blue
Dark blue = nuclei/ribosomes
Pale blue = cytoplasm
Bright purple = cartliage/matrix/mast cell and GAG rich
What is this slide stained with?
What stains:
Pink Red
Yellow/Olive green
Dark brown

Van giesons trichrome with haemotoxylin counter stain
Pink red = collagen
Cell cytoplasm = yellow/olive green
Nuclei = black
Elastic tissue = dark brown
What is this slide stained with?
What stains blue with this stain?
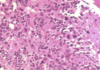
Haemotoxylin
- Nuclei
- RNA
What is this slide stained with?
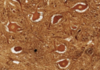
Silver stain
Describe neurones?
Neurones are large
25-60 microns
Because of the thickness of slides cannot see all processes
1 to 5 dentritic processes
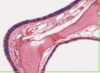
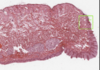
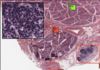
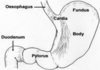
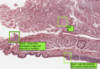
Where is the epithelium from?
What type of epithelium is it and describe it?
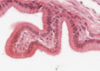
From the gall bladder
Simple columnar
- Height > width
- Oval nucelus
- Longer axis perpendicular to base of the cell
- Often microvilli or cilia at the apical membrane
- GUT ENTEROCYTES and RESPIRATORY TRACT
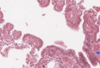
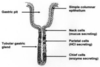
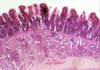
What type of epithelium is this?
Describe?
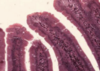
Intestinal epithelium
- Enterocytes with goblet cells
- Epithelia sit on BM permeability barrier between epithelium and connective tissue
- Microvilli at the apical surface (brush border)
- Brush border increases surface area
- Small intestine = simple columnar
Larger intestine > goblet cells
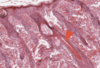
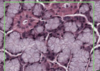
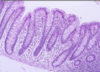
What is this a slide of?
What stain has been used?
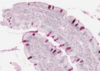
Microvilli/intestinal
Stained with PAS and haematoxylin
- Microvilli with carbohydrate rich glcocaylx
- Goblet cells and basement membrane rich in hexose
- The stain is magenta
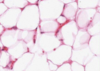
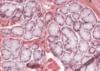
What type of epithelium is this?

Cuboidal epithelium
- Square
- Round nucleus
- Ducts at exocrine glands: sweat glands, salivary, pancreas and kidney tissue
What type of epithelium is this?
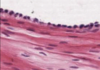
Squamous (serosa at outer wall of intestine)
- Outer surface of most thoracic and abdominal organs
- Simple squamous epthielum = serosa
- Also lines pleura and peritoneal cavities
- Air sacs of lungs
- Flattened
- Cylindrical ellpitical nuclei at the base
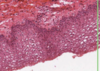
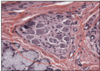
What type of epthielium is this where is it founf?
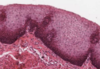
Stratified squamous non keratinsing epithlium (left is mouth)
Found in:
- Mouth
- Throat
- Oesophagus
- Anus
- Vagina
What type of epthielium is this?
Where is it found
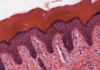
Keratinised stratified squamous epithelium
- Epidermis
- Lower layers are similar to stratified squamous
- Upper layers synthesise a unique collection of proteins - interact with cytoskeleton of cell to produce keratin
- Keratin: a dense protein that fills the cytoplasms of cells = tough and waterproof
- When the cell is full of keratin they die and are sloughed off
Left = Hairless skin at lower lip
pink = dead keratinised squames
Boundary later with blue keratohyaline granules STRATUM GRANULOSUM
What type of epthlium is this?
Where is it found?

Pseudostratified
Multilayered but stretches when flattened
Slide = trachea
Also found in urinary tract
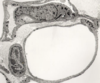
What is this slide showing?
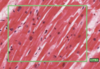
Caridiac muscle (myocardium)
- Branching chains of cardiac myocytes (15 x 100 microns)
- Striations (myofibrils and repeat sarcolemmas)
- Dark intercalated disks
How does cardiac muscle differ from skeletal?
Structurally
- Branched mononuclear with no stem cells
Phyisologically
- Contract and relax without rest, secrete hormones (ANP when stretech excessively, increases water/Na+/K+ excretion and inhibits RAAS)
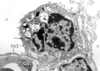
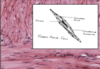
What is this slide showing?

Intercalated disk
With desmosomes and adherant junctions (stick)
With gap junctions (electrical coupling)
Disc = Black
Myofibril = Blue/black
MIT/RBC = red
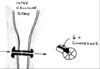
What are the functions of the intercalated discs?
Desomosomes anchor one cardiac muscle to the next by immediate cytoskeleton filaments
Gap junctions allow ion transfer between cardiac muscle - electrochemical coupling not cardiac conduction!
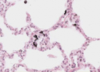
What is this slide showing?

Purkinje fibres (with PAS proceedure - magenta)
- Large modified muscles
- Large vacuoles
- Few myofibrils therefore pale H and E
- Stores of glyocogen (PAS)
Cardiac conduction
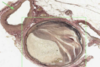
Describe valves?
- Thick collagen with occasional elastic tissue
- Both surfaces with endothelial cells
- Chordae tendinae = Fibrous