Histopathology Flashcards
(525 cards)
What are the role of neutrophils?
Acute inflammation - first responses
Describe the appearance of neutrophils.
Multi-lobed
Describe the recruitment of neutrophils.
Margination - move into margin of blood vessels, affected by blood flow Rolling - not fully adhesive Adhesion - fully adhesive Transmigration/diapedesis - either through or between endo cells and through BM
What are the role of lymphocytes and plasma cells?
Chronic inflammation
Describe the appearance of lymphocytes.
Little cytoplasm Big nucleus
What are the role of eosinophils?
Allergic reactions Parasitic infections Tumours e.g. Hodgkin’s disease (reaction to tumours
Describe the appearance of eosinophils.
Bi-lobed nucleus Red granules
What are the roles of mast cells?
Allergic reactions
Describe the appearance of mast cells.
Very large and prominent granules
What are the roles of macrophages?
- Late acute inflammation
- Chronic inflammation - granulomas etc
- Naturally phagocytic - in chronic inflammation they become secretory
Describe the appearance of macrophages.
- Small nucleus
- Lots of cytoplasm - becomes even more with increased ER and golgi bodies when secretory in chronic inflammation
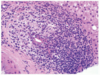
What is a granuloma?
- Organised collection of activated macrophages (epithelioid macrophages)
- Secretory macrophages
- Associated with infections e.g. TB, leprosy, fungal infection
Define carcinoma.
Malignant tumours of epithelial cells
What are the features of squamous cell carcinoma?
- Intercellular bridges
- Keratin production (not in all)
- Skin, head and neck, top oesophagus, cervix, vagina, anus
What are the features of adenocarcinoma?
- Forms from glands
- Mucin production
- Lung, breast, stomach, bottom oesophagus, colon, pancreas, sweat glands
What are the features of transitional cell carcinoma?
Multi-layered Urinary tract - e.g. bladder, ureter
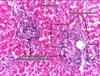
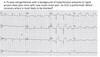
What type of tumour are these images? Describe why.

Squamous cell carcinoma
- Keratin at the top
- Intracellular bridges - parallel lines between cells
- Swirls of keratin
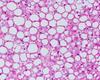
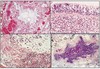
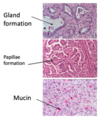
What type of tumour are these images? Describe why.

Adenocarcinoma
- Mucin stain with glands - show up blue
- Dark irregular nuclei still froming gland-like structure
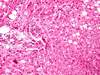
What type of tumour are these images? Describe why.

Normal glandular epithelium with crypts
What are the 2 types of stains?
Histo-chemical
Immuno-histochemical
Describe histo-chemical stains and give some examples.
Chemical reaction between stain and specific component of tissue
Product of reaction has specific colour or property that can be identified
- Haematoxylin and eosin, Prussian blue iron, Congo red
What is the haematoxylin and eosin stain used for?
Most common histochemical stain to visualise cells for light microscopy
- Used in cancer diagnosis
What is the Prussian blue iron stain used for?
To detect the prescence of iron in tissue
- Haemachromatosis
What is the Congo red stain used for?
Amyloid