History + Exam Flashcards
(26 cards)
Cough most common diagnosis?

Cough acute vs chronic?
Acute = < 3 weeks
chronic = > 8 weeks
Cough constant or intermittent?
intermittent suggests extrinsic trigger
constant is likely intrinsic.
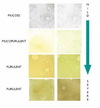
Cough Productive or dry?
sputum indicates inflammation or infection,
COPD have chronically inflamed airways and often produce white or clear sputum.
Infection is yellow or green.
Large volumes, often green or rusty may be coughed up by bronchiectasis and lung abscesses.
Cough blood streaked sputum?
suggests infection or bronchiectasis
Cough pink frothy sputum?
suggests pulmonary oedema

Cough frank blood (haemoptysis)?
TB, lung cancer, pulmonary embolus, bronchiectasis and rare causes (e.g. granulomatosis with polyangiitis, Goodpasture’s syndrome).
Cough timing/character (5)?
asthma is typically worse at night and early morning.
A bovine cough is characteristic of cord paralysis.
A dry cough is usually bronchitis (commonly viral) or interstitial lung disease.
A gurgling/wet cough is bronchiectasis.
Pertussis infection causes a ‘whooping’ cough.
Cough triggering factors environmental irritants?
smoking, occupation, pets, house change
Cough triggering factors PMH (5)?
asthma, GORD, Rhinitis/sinusitis, heart failure, chest infection
Cough triggering factors drug history?
ACE inhibitors can cause a cough.
Cough triggering factors travel?
somewhere TB is common
Cough triggering factors close contants?
someone else with a cough might give them TB.
Cough + Fevers, night sweats, rigors, weight loss?
malignancy, TB, or other severe infection
Cough + breathlessness (4)?
asthma, COPD, pneumonia, pulmonary oedema.
Cough + chest pain, particularly pleuritic (4)?
may indicate pneumonia, pneumothorax, pulmonary embolism, can also be muscle strain due to coughing or fractured rib from trauma.
Cough + wheeze
suggests obstruction such as found with asthma, COPD, tumours.
Cough + frequent throat clearing?
Rhinitis

Cough exam systemic features?
febrile, sweating, tachycardic.
Cough exam respiratory distress?
tachypnoea, difficulty breathing, accessory muscles, peripherally cyanosed, confused.
Cough exam tender cervical lymphadenopathy?
upper respiratory tract infection.

Cough exam lungs?
reduced chest expansion, breath sounds (reduced in effusion, bronchial sounding in pneumonia),
vocal resonance (increased in consolidation, reduced in pleural effusion).
Cough exam chest wall deformities?
hyper expansion or barrel chest.
Cough exam intercostal recession?
sign of severe COPD



