HNN Flashcards
(113 cards)
boundaries carotid triangle
digastric, omohyoid, scm s
boundaries post and anterior triangle
post- SCM, trapezius, clavicle
anterior- mandible, midline, SCM
tonsils in waldeyers ring
palatine, pharyngeal, lingual, tubal
muscles facial expression all
obicularis oris (oribital= tight), occipitofrontalis, obiculatis ores, buccinator, zygomaticus, risorius, platysma
mastication muscles (which elevate, depress, retract/protract mandible?)
masseter (elevate), temporalis (retract and elevate), pterygoids (elevate and protract)
which is more anterior, bregma or lambda?
bregma
what is A

foramen retundum
what is B

foramen ovale
what is C

IAM
what is D

jugular foramen
what is E
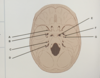
foramen lacerum
what is F

foramen spinosum
what is G
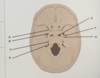
carotid canal
branches of internal carotid artery
anterior and middle cerebral, opthalmic (which gives supratroclear and supraorbital) and post. communicantes
branches external carotid artery
Some Anatomists Like Freaking Out Poor Medical Students
Superior thyroid, ascending pharyngeal, lingual, facial, occipital, posterior auricular, maxillary, superficial temporal
which is more lateral, subclavian or common carotid
subclavian
describe route of facial drainage
- supraorbital and supratrochlear
- angular vein
- facial vein
- common facial vein
- IVJ
describe route of scalp drainage
- superficial temporal
- occipital joins to form retromandibular
- posterior auricular joins to form EJV
- subclavian
compare what drains into cavernous sinus vs pterygoid venous plexus
cavernous sinus- superior and inferior opthalmic artery
pterygoid venous plexus- deep facial vein
compare bridging and emissary veins
Emissay veins are Exterior to bridging veins. they connect extracranial veins to DVS
bridging- intracranial viens to DVS
compare causes of intracranial haemorrages
extradural- middle meningeal artery
subdural- bridging veins
subarachnoid- circle of willis
role parietal, occipital, temporal and frontal lobes
parietal- spacial awareness, somatosensory perception
occipital- vision
temporal- smell and memory
frontal- higher cognition and voluntary motor control
what makes up brainstem
midbrain, pons and medulla
role of midbrain, pons and medulla
midbrain- movement of eye, auditory and visual processing
pons- feeding and sleep
medulla- CVS/resp